Expression and significance of circulating microRNA-31 in lung cancer patients
- PMID: 25765717
- PMCID: PMC4362487
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.893213
Expression and significance of circulating microRNA-31 in lung cancer patients
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the expression level of circulating microRNA-31(miRNA-31) in lung cancer patients and its clinical significance.
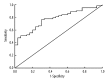
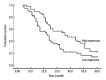
Material and methods: Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR was utilized to detect the circulating miRNA-31 expression levels in 300 lung cancer patients and 300 health control subjects. The ROC curve was drawn to evaluate the diagnostic value of the circulating miRNA-31 expression levels in lung cancer. The 300 lung cancer patients were divided into a miRNA-31 low-expression group and a miRNA-31 high-expression group. A survival curve was drawn according to the Kaplan-Meier method to evaluate the prognostic value of the circulating microRNA-31 expression levels for lung cancer.
Results: The circulating miRNA-31 expression levels in the lung cancer patients (l.88±0. 67) increased significantly (P<0.001) compared to the healthy controls (0.58±0. 44). The area under the ROC curve drawn according to the circulating miRNA-31 expression levels was 0.785 (95% CI=0.486-0.763). When the critical value was 1.27, the sensitivity and specificity for lung cancer diagnosis according to the circulating miRNA-31 expression levels were 0.769 and 0.745, respectively. The difference in the survival curve between the miRNA-31 low-expression group (123 cases) and high-expression group (177 cases) was statistically significant (P=0.004). Median survival period of the low-expression group (38.44 months) was longer than that of the high-expression group (25.23 months).
Conclusions: miRNA-31 may be a molecular marker for the diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of primary lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating MicroRNA-21, MicroRNA-23a, and MicroRNA-125b as Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Burkitt Lymphoma in Children.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Dec 19;22:4992-5002. doi: 10.12659/msm.897417. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27991481 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Circulatory miRNA-21 as an Efficient Non-Invasive Biomarker for the Screening of Lung Cancer Patients.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Sep 26;19(9):2607-2611. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.9.2607. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 30256067 Free PMC article.
-
Serum microRNA-365 in combination with its target gene TTF-1 as a non-invasive prognostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Oct;75:185-90. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.07.026. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26337230
-
Clinical significance of circulating miRNA detection in lung cancer.Med Oncol. 2016 May;33(5):41. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0757-5. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27034265 Review.
-
[Circulating microRNAs in lung cancer: prospects for diagnostics, prognosis and prediction of antitumor treatment efficiency].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2015 Jan-Feb;49(1):55-66. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2015. PMID: 25916110 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Improved low-rank matrix recovery method for predicting miRNA-disease association.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 20;7(1):6007. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06201-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28729528 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of Circulating microRNAs for Early Detection of Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;14(17):4221. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174221. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077759 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Serum From Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients Induces Altered MicroRNA and Target Gene Expression Profile in Treated Cells.Front Oncol. 2018 Jun 11;8:217. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00217. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29942793 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miR-31 as an effective biomarker for detection and prognosis of human cancer: a meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 25;8(17):28660-28671. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15638. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28404921 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating noncoding RNAs: promising biomarkers in liquid biopsy for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of NSCLC.Discov Oncol. 2023 Aug 1;14(1):142. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00686-3. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37526759 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sheel AR, McShane J, Poullis MP. Survival of patients with or without symptoms undergoing potentially curative resections for primary lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95(1):276–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

