Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy in a Chinese pedigree: A case report using brain magnetic resonance imaging and biospy
- PMID: 25767504
- PMCID: PMC4353120
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.03.012
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy in a Chinese pedigree: A case report using brain magnetic resonance imaging and biospy
Abstract
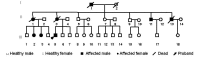
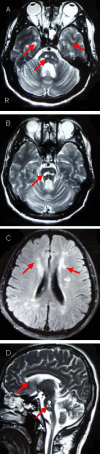
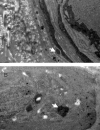
The present study enrolled a Chinese family that comprised 34 members and spanned three generations. Eight members were diagnosed with cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, and disease diagnoses corresponded with autosomal incomplete dominance inheritance. The primary clinical manifestations included paralysis, dysarthria, and mild cognitive deficits. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed diffuse leukoencephalopathy with involvement of bilateral anterior temporal lobes, in particular the pons. In addition, multiple cerebral infarction was identified in the proband. Sural nerve biopsy findings of the proband revealed granular osmophilic material deposits in the extracellular matrix, which were adjacent to smooth muscle cells of dermal arterioles. Screening exons 2-4 for NOTCH 3 mutations by direct sequencing did not reveal any abnormalities.
Keywords: NOTCH 3; cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy; dysarthria; granular osmophilic material; leukoencephalopathy; paresis; subcortical infarcts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal involvement in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL).Clin Nephrol. 2007 Mar;67(3):182-7. doi: 10.5414/cnp67182. Clin Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17390743
-
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) in a Chinese family: clinical, radiological and skin biopsy features.J Clin Neurosci. 2004 Apr;11(3):304-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2003.05.007. J Clin Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14975424
-
[A cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy pedigree: clinical pathology, neuroimaging and molecular genetics studies].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011 Nov;42(6):866-9. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011. PMID: 22332560 Chinese.
-
[Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL)].Rinsho Byori. 2009 Mar;57(3):242-51. Rinsho Byori. 2009. PMID: 19363995 Review. Japanese.
-
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL).Panminerva Med. 2004 Dec;46(4):265-76. Panminerva Med. 2004. PMID: 15876982 Review.
References
-
- Joutel A, Corpechot C, Ducros A, et al. Notch3 mutations in CADASIL, a hereditary adult-onset condition causing stroke and dementia. Nature. 1996;383(6602):707–710. - PubMed
-
- Baudrimont M, Dubas F, Joutel A, et al. Autosomal dominant leukoencephalopathy and subcortical ischemic stroke. A clinicopathological study. Stroke. 1993;24(1):122–125. - PubMed
-
- Auer DP, Pütz B, Gössl C, et al. Differential lesion patterns in CADASIL and sporadic subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: MR imaging study with statistical parametric group comparison. Radiology. 2001;218(2):443–451. - PubMed
-
- Markus HS, Martin RJ, Simpson MA, et al. Diagnostic strategies in CADASIL. Neurology. 2002;59(8):1134–1138. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
