Approach to neurometabolic diseases from a pediatric neurological point of view
- PMID: 25767534
- PMCID: PMC4322494
Approach to neurometabolic diseases from a pediatric neurological point of view
Abstract
Objective Neurometabolic disorders are an important group of diseases that mostly are presented in newborns and infants. Neurological manifestations are the prominent signs and symptoms in this group of diseases. Seizures are a common sign and are often refractory to antiepileptic drugs in untreated neurometabolic patients. The onset of symptoms for neurometabolic disorders appears after an interval of normal or near normal growth and development.Additionally, affected children may fare well until a catabolic crisis occurs. Patients with neurometabolic disorders during metabolic decompensation have severe clinical presentation, which include poor feeding, vomiting, lethargy, seizures, and loss of consciousness. This symptom is often fatal but severe neurological insult and regression in neurodevelopmental milestones can result as a prominent sign in patients who survived. Acute symptoms should be immediately treated regardless of the cause. A number of patients with neurometabolic disorders respond favorably and, in some instances, dramatically respond to treatment. Early detection and early intervention is invaluable in some patients to prevent catabolism and normal or near normal neurodevelopmental milestones. This paper discusses neurometabolic disorders, approaches to this group of diseases (from the view of a pediatric neurologist), clinical and neurological manifestations, neuroimaging and electroencephalography findings, early detection, and early treatment.
Keywords: Early detection; Early treatment; Electroencephalography; Neurological manifestation; Neurometabolic disorders.
Figures
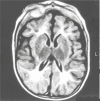
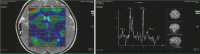
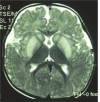
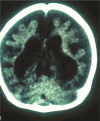

Similar articles
-
Neurometabolic Diagnosis in Children who referred as Neurodevelopmental Delay (A Practical Criteria, in Iranian Pediatric Patients).Iran J Child Neurol. 2016 Summer;10(3):73-81. Iran J Child Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27375759 Free PMC article.
-
Eye motor manifestations in children with neurometabolic disorders.J Formos Med Assoc. 2022 Apr;121(4):736-748. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Formos Med Assoc. 2022. PMID: 34561118 Review.
-
Methylmalonic acidemia: diagnosis and neuroimaging findings of this neurometabolic disorder (an Iranian pediatric case series).Iran J Child Neurol. 2013 Summer;7(3):63-6. Iran J Child Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24665309 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Tailored Pediatric Rehabilitation Protocol on Children With Neurometabolic Disorder: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Mar 28;16(3):e57115. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57115. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38681474 Free PMC article.
-
Approach to Neurological Channelopathies and Neurometabolic Disorders in Newborns.Life (Basel). 2021 Nov 16;11(11):1244. doi: 10.3390/life11111244. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolism navigates neural cell fate in development, aging and neurodegeneration.Dis Model Mech. 2021 Aug 1;14(8):dmm048993. doi: 10.1242/dmm.048993. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Dis Model Mech. 2021. PMID: 34345916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurometabolic Diagnosis in Children who referred as Neurodevelopmental Delay (A Practical Criteria, in Iranian Pediatric Patients).Iran J Child Neurol. 2016 Summer;10(3):73-81. Iran J Child Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27375759 Free PMC article.
-
Microcephaly in Neurometabolic Diseases.Children (Basel). 2022 Jan 11;9(1):97. doi: 10.3390/children9010097. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biallelic loss of function variants in PPP1R21 cause a neurodevelopmental syndrome with impaired endocytic function.Hum Mutat. 2019 Mar;40(3):267-280. doi: 10.1002/humu.23694. Epub 2018 Dec 25. Hum Mutat. 2019. PMID: 30520571 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic impact of whole exome sequencing in neurometabolic disorders in Syrian children: a single center experience.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 May 7;20(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03732-1. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40336053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Filiano JJ. Neurometabolic Disease in the Newborn. ClinPerinatol. 2006;33:411–479. - PubMed
-
- Van Karnebeek CDM, Stockler S. Treatable inborn errors of metabolism causing intellectual disability: A systematic literature review. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 2012;105:369–381. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Salam GMH, Abdel-Kader AA, Effat L, Gouda A, Hindawy A, El-Gammal MA. Clinical, Electroencephalographic (EEG), Neuroradiological and Molecular Correlations in Late-Detected Phenylketonuria (PKU) Patients. Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. 2005;42(2):391–406.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
