CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β is dispensable for development of lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 25767874
- PMCID: PMC4358974
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120647
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β is dispensable for development of lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
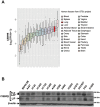
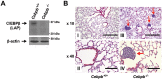
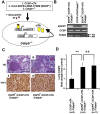
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Although disruption of normal proliferation and differentiation is a vital component of tumorigenesis, the mechanisms of this process in lung cancer are still unclear. A transcription factor, C/EBPβ is a critical regulator of proliferation and/or differentiation in multiple tissues. In lung, C/EBPβ is expressed in alveolar pneumocytes and bronchial epithelial cells; however, its roles on normal lung homeostasis and lung cancer development have not been well described. Here we investigated whether C/EBPβ is required for normal lung development and whether its aberrant expression and/or activity contribute to lung tumorigenesis. We showed that C/EBPβ was expressed in both human normal pneumocytes and lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. We found that overall lung architecture was maintained in Cebpb knockout mice. Neither overexpression of nuclear C/EBPβ nor suppression of CEBPB expression had significant effects on cell proliferation. C/EBPβ expression and activity remained unchanged upon EGF stimulation. Furthermore, deletion of Cebpb had no impact on lung tumor burden in a lung specific, conditional mutant EGFR lung cancer mouse model. Analyses of data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) revealed that expression, promoter methylation, or copy number of CEBPB was not significantly altered in human lung adenocarcinoma. Taken together, our data suggest that C/EBPβ is dispensable for development of lung adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Airway epithelial cell differentiation during lung organogenesis requires C/EBPα and C/EBPβ.Dev Dyn. 2012 May;241(5):911-23. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.23773. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Dev Dyn. 2012. PMID: 22411169
-
C/EBPβ regulates homeostatic and oncogenic gastric cell proliferation.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Dec;94(12):1385-1395. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1447-7. Epub 2016 Aug 13. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27522676 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBPβ Is a Transcriptional Regulator of Wee1 at the G₂/M Phase of the Cell Cycle.Cells. 2019 Feb 11;8(2):145. doi: 10.3390/cells8020145. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30754676 Free PMC article.
-
Lung epithelial-C/EBPβ contributes to LPS-induced inflammation and its suppression by formoterol.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jun 22;423(1):134-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.05.096. Epub 2012 May 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22634316
-
Emerging functions of C/EBPβ in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 25;13:1111522. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1111522. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36761942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutant Proteomics of Lung Adenocarcinomas Harboring Different EGFR Mutations.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 25;10:1494. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01494. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32983988 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β-induced α-SMA expression is mediated by C/EBPβ acetylation in human alveolar epithelial cells.Mol Med. 2021 Mar 4;27(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00283-6. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33663392 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBPβ deficiency enhances the keratinocyte innate immune response to direct activators of cytosolic pattern recognition receptors.Innate Immun. 2023 Jan;29(1-2):14-24. doi: 10.1177/17534259231162192. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Innate Immun. 2023. PMID: 37094088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2014;64(1):9–29. - PubMed
-
- Cersosimo RJ. Lung cancer: a review. American journal of health-system pharmacy: AJHP: official journal of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. 2002;59(7):611–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

