Sorption and release of organics by primary, anaerobic, and aerobic activated sludge mixed with raw municipal wastewater
- PMID: 25768429
- PMCID: PMC4359093
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119371
Sorption and release of organics by primary, anaerobic, and aerobic activated sludge mixed with raw municipal wastewater
Abstract
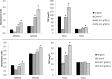
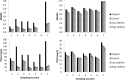
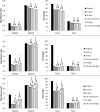
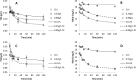
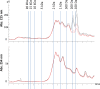
New activated sludge processes that utilize sorption as a major mechanism for organics removal are being developed to maximize energy recovery from wastewater organics, or as enhanced primary treatment technologies. To model and optimize sorption-based activated sludge processes, further knowledge about sorption of organics onto sludge is needed. This study compared primary-, anaerobic-, and aerobic activated sludge as sorbents, determined sorption capacity and kinetics, and investigated some characteristics of the organics being sorbed. Batch sorption assays were carried out without aeration at a mixing velocity of 200 rpm. Only aerobic activated sludge showed net sorption of organics. Sorption of dissolved organics occurred by a near-instantaneous sorption event followed by a slower process that obeyed 1st order kinetics. Sorption of particulates also followed 1st order kinetics but there was no instantaneous sorption event; instead there was a release of particles upon mixing. The 5-min sorption capacity of activated sludge was 6.5±10.8 mg total organic carbon (TOC) per g volatile suspend solids (VSS) for particulate organics and 5.0±4.7 mgTOC/gVSS for dissolved organics. The observed instantaneous sorption appeared to be mainly due to organics larger than 20 kDa in size being sorbed, although molecules with a size of about 200 Da with strong UV absorbance at 215-230 nm were also rapidly removed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
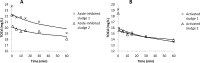
References
-
- Arden E, Lockett WT. Experiments on the oxidation of sewage without the aid of filters. J Soc Chem Ind. 1914; 33: 523–539.
-
- Metcalf & Eddy Inc., Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, Stensel HD. Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse 4th Ed. McGraw-Hill; 2004.
-
- Yamamoto K, Hiasa M, Mahmood T, Matsuo T. Direct solid-liquid separation using hollow fiber membrane in an activated sludge aeration tank. Water Sci Technol. 1989; 21: 43–54.
-
- Ullrich AH, Smith MW. The biosorption process of sewage and waste treatment. Sewage Ind Waste. 1951; 23: 1248–1253.
-
- Versprille A, Zuurveen B, Stein T. The A-B process: A novel wastewater treatment system. Water Sci Technol. 1985; 17: 235–246.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

