Human disease modeling reveals integrated transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of NOTCH1 haploinsufficiency
- PMID: 25768904
- PMCID: PMC4359747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.035
Human disease modeling reveals integrated transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of NOTCH1 haploinsufficiency
Abstract
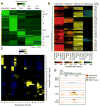
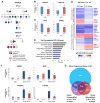
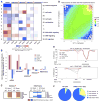
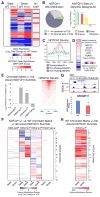
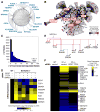
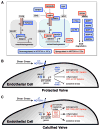
The mechanisms by which transcription factor haploinsufficiency alters the epigenetic and transcriptional landscape in human cells to cause disease are unknown. Here, we utilized human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived endothelial cells (ECs) to show that heterozygous nonsense mutations in NOTCH1 that cause aortic valve calcification disrupt the epigenetic architecture, resulting in derepression of latent pro-osteogenic and -inflammatory gene networks. Hemodynamic shear stress, which protects valves from calcification in vivo, activated anti-osteogenic and anti-inflammatory networks in NOTCH1(+/+), but not NOTCH1(+/-), iPSC-derived ECs. NOTCH1 haploinsufficiency altered H3K27ac at NOTCH1-bound enhancers, dysregulating downstream transcription of more than 1,000 genes involved in osteogenesis, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Computational predictions of the disrupted NOTCH1-dependent gene network revealed regulatory nodes that, when modulated, restored the network toward the NOTCH1(+/+) state. Our results highlight how alterations in transcription factor dosage affect gene networks leading to human disease and reveal nodes for potential therapeutic intervention.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
What Endothelial Cells from Patient iPSCs Can Tell Us about Aortic Valve Disease.Cell Stem Cell. 2015 May 7;16(5):455-7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.04.006. Cell Stem Cell. 2015. PMID: 25957898
References
-
- Alatalo SL, Halleen JM, Hentunen TA, Mönkkönen J, Väänänen HK. Rapid screening method for osteoclast differentiation in vitro that measures tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b activity secreted into the culture medium. Clin Chem. 2000;46:1751–1754. - PubMed
-
- Bragdon B, Moseychuk O, Saldanha S, King D, Julian J, Nohe A. Bone morphogenetic proteins: a critical review. Cell Sig. 2011;23:609–620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

