Hepatitis C virus RNA functionally sequesters miR-122
- PMID: 25768906
- PMCID: PMC4386883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.025
Hepatitis C virus RNA functionally sequesters miR-122
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) uniquely requires the liver-specific microRNA-122 for replication, yet global effects on endogenous miRNA targets during infection are unexplored. Here, high-throughput sequencing and crosslinking immunoprecipitation (HITS-CLIP) experiments of human Argonaute (AGO) during HCV infection showed robust AGO binding on the HCV 5'UTR at known and predicted miR-122 sites. On the human transcriptome, we observed reduced AGO binding and functional mRNA de-repression of miR-122 targets during virus infection. This miR-122 "sponge" effect was relieved and redirected to miR-15 targets by swapping the miRNA tropism of the virus. Single-cell expression data from reporters containing miR-122 sites showed significant de-repression during HCV infection depending on expression level and site number. We describe a quantitative mathematical model of HCV-induced miR-122 sequestration and propose that such miR-122 inhibition by HCV RNA may result in global de-repression of host miR-122 targets, providing an environment fertile for the long-term oncogenic potential of HCV.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

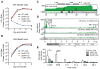
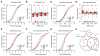
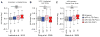
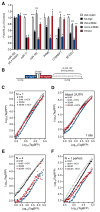
Comment in
-
Hepatitis C virus addiction to liver miR-122 takes its Toll on the host.Hepatology. 2015 Nov;62(5):1633-5. doi: 10.1002/hep.27947. Epub 2015 Jul 25. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 26096908 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chang J, Nicolas E, Marks D, Sander C, Lerro A, Buendia MA, Xu C, Mason WS, Moloshok T, Bort R, et al. miR-122, a mammalian liver-specific microRNA, is processed from hcr mRNA and may downregulate the high affinity cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1. RNA Biol. 2004;1:106–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 NS081706/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS034389/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091707/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI090055/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI075099/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NS081706/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034389/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA057973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI090055/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI075099/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AI072613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK085713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI099284/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI099284/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK090576/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI091707/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

