Synaptopathy in the noise-exposed and aging cochlea: Primary neural degeneration in acquired sensorineural hearing loss
- PMID: 25769437
- PMCID: PMC4567542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.02.009
Synaptopathy in the noise-exposed and aging cochlea: Primary neural degeneration in acquired sensorineural hearing loss
Abstract
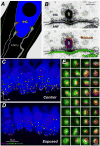
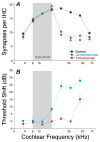
The classic view of sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is that the "primary" targets are hair cells, and that cochlear-nerve loss is "secondary" to hair cell degeneration. Our recent work in mouse and guinea pig has challenged that view. In noise-induced hearing loss, exposures causing only reversible threshold shifts (and no hair cell loss) nevertheless cause permanent loss of >50% of cochlear-nerve/hair-cell synapses. Similarly, in age-related hearing loss, degeneration of cochlear synapses precedes both hair cell loss and threshold elevation. This primary neural degeneration has remained hidden for three reasons: 1) the spiral ganglion cells, the cochlear neural elements commonly assessed in studies of SNHL, survive for years despite loss of synaptic connection with hair cells, 2) the synaptic terminals of cochlear nerve fibers are unmyelinated and difficult to see in the light microscope, and 3) the degeneration is selective for cochlear-nerve fibers with high thresholds. Although not required for threshold detection in quiet (e.g. threshold audiometry or auditory brainstem response threshold), these high-threshold fibers are critical for hearing in noisy environments. Our research suggests that 1) primary neural degeneration is an important contributor to the perceptual handicap in SNHL, and 2) in cases where the hair cells survive, neurotrophin therapies can elicit neurite outgrowth from spiral ganglion neurons and re-establishment of their peripheral synapses. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled <Auditory Synaptology>.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bauer CA, Brozoski TJ, Myers K. Primary afferent dendrite degeneration as a cause of tinnitus. Journal of neuroscience research. 2007;85:1489–98. - PubMed
-
- Bohne BA, Harding GW. Degeneration in the cochlea after noise damage: primary versus secondary events. Am J Otol. 2000;21:505–9. - PubMed
-
- Bourien J, Tang Y, Batrel C, Huet A, Lenoir M, Ladrech S, Desmadryl G, Nouvian R, Puel JL, Wang J. Contribution of auditory nerve fibers to compound action potential of the auditory nerve. J Neurophysiol. 2014;112:1025–39. - PubMed
-
- Costalupes JA, Young ED, Gibson DJ. Effects of continuous noise backgrounds on rate response of auditory nerve fibers in cat. J Neurophysiol. 1984;51:1326–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

