The endogenous cell-fate factor dachshund restrains prostate epithelial cell migration via repression of cytokine secretion via a cxcl signaling module
- PMID: 25769723
- PMCID: PMC4433595
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0611
The endogenous cell-fate factor dachshund restrains prostate epithelial cell migration via repression of cytokine secretion via a cxcl signaling module
Abstract
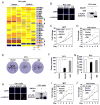
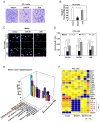
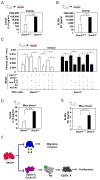
Prostate cancer is the second leading form of cancer-related death in men. In a subset of prostate cancer patients, increased chemokine signaling IL8 and IL6 correlates with castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). IL8 and IL6 are produced by prostate epithelial cells and promote prostate cancer cell invasion; however, the mechanisms restraining prostate epithelial cell cytokine secretion are poorly understood. Herein, the cell-fate determinant factor DACH1 inhibited CRPC tumor growth in mice. Using Dach1(fl/fl)/Probasin-Cre bitransgenic mice, we show IL8 and IL6 secretion was altered by approximately 1,000-fold by endogenous Dach1. Endogenous Dach1 is shown to serve as a key endogenous restraint to prostate epithelial cell growth and restrains migration via CXCL signaling. DACH1 inhibited expression, transcription, and secretion of the CXCL genes (IL8 and IL6) by binding to their promoter regulatory regions in chromatin. DACH1 is thus a newly defined determinant of benign and malignant prostate epithelium cellular growth, migration, and cytokine abundance in vivo.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: R.G.P. holds major (> $10,000) ownership interests in, and serves as CSO/Founder of the biopharmaceutical companies ProstaGene, LLC and AAA Phoenix, Inc. R.G.P. additionally holds ownership interests (value unknown) for several granted and submitted patent applications.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. 2010 Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberger MA. The Current Knowledge of Hormonal Therapy in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. In: Pestell RG, Nevalainen MT, editors. Prostate Cancer - Signaling Networks, Genetics, and New Treatment Strategies. Santa Monica, CA: Humana Press; 2008. pp. 339–354.
-
- Heinlein CA, Chang C. Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 2004;25:276–308. - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto H, Messing EM, Chang C. Does androgen deprivation improve treatment outcomes in patients with low-risk and intermediate-risk prostate cancer? Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2005;2:236–237. - PubMed
-
- Chang CS, Kokontis J, Liao ST. Molecular cloning of human and rat complementary DNA encoding androgen receptors. Science. 1998;240:324–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

