Post-PET ultrasound improves specificity of 18F-FDG-PET for recurrent differentiated thyroid cancer while maintaining sensitivity
- PMID: 25770086
- PMCID: PMC4768638
- DOI: 10.1177/0284185115574298
Post-PET ultrasound improves specificity of 18F-FDG-PET for recurrent differentiated thyroid cancer while maintaining sensitivity
Abstract
Background: Positron emission tomography (PET) using fluor-18-deoxyglucose (18F-FDG) with or without computed tomography (CT) is generally accepted as the most sensitive imaging modality for diagnosing recurrent differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) in patients with negative whole body scintigraphy with iodine-131 (I-131).
Purpose: To assess the potential incremental value of ultrasound (US) over 18F-FDG-PET-CT.
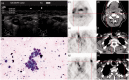
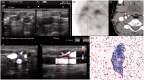
Material and methods: Fifty-one consecutive patients with suspected recurrent DTC were prospectively evaluated using the following multimodal imaging protocol: (i) US before PET (pre-US) with or without fine needle biopsy (FNB) of suspicious lesions; (ii) single photon emission computed tomography (≥3 GBq I-131) with co-registered CT (SPECT-CT); (iii) 18F-FDG-PET with co-registered contrast-enhanced CT of the neck; (iv) US in correlation with the other imaging modalities (post-US). Postoperative histology, FNB, and long-term follow-up (median, 2.8 years) were taken as composite gold standard.
Results: Fifty-eight malignant lesions were identified in 34 patients. Forty lesions were located in the neck or upper mediastinum. On receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis, 18F-FDG-PET had a limited lesion-based specificity of 59% at a set sensitivity of 90%. Pre-US had poor sensitivity and specificity of 52% and 53%, respectively, increasing to 85% and 94% on post-US, with knowledge of the PET/CT findings (P < 0.05 vs. PET and pre-US). Multimodal imaging changed therapy in 15 out of 51 patients (30%).
Conclusion: In patients with suspected recurrent DTC, supplemental targeted US in addition to 18F-FDG-PET-CT increases specificity while maintainin sensitivity, as non-malignant FDG uptake in cervical lesions can be confirmed.
Keywords: Head/neck; PET; computed tomography (CT); neoplasms; thyroid; ultrasound.
© The Foundation Acta Radiologica 2015.
Figures


References
-
- Cancer Registry of Norway. Cancer in Norway 2012. Cancer incidence, mortality, survival and prevalence in Norway, Oslo: Cancer Registry of Norway, 2014. Available at: http://www.kreftregisteret.no/en/.
-
- Brauckhoff M, Machens A, Thanh PN, et al. Impact of extent of resection for thyroid cancer invading the aerodigestive tract on surgical morbidity, local recurrence, and cancer-specific survival. Surgery 2010; 148: 1257–1266. - PubMed
-
- Biermann M, Pixberg M, Riemann B, et al. Clinical outcomes of adjuvant external-beam radiotherapy for differentiated thyroid cancer - Results after 874 patient-years of follow-up in the MSDS-trial. Nuklearmedizin 2009; 48: 89–98. - PubMed
-
- Maxon HR. Detection of residual and recurrent thyroid cancer by radionuclide imaging. Thyroid 1999; 9: 443–446. - PubMed
-
- Durante C, Haddy N, Baudin E, et al. Long-term outcome of 444 patients with distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma: benefits and limits of radioiodine therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 2892–2899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

