Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) promotes the pro-survival activity of 14-3-3ζ via deacetylation of lysines within the 14-3-3ζ binding pocket
- PMID: 25770209
- PMCID: PMC4432270
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.607580
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) promotes the pro-survival activity of 14-3-3ζ via deacetylation of lysines within the 14-3-3ζ binding pocket
Abstract
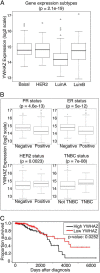
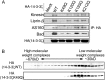
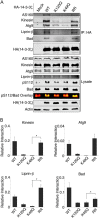
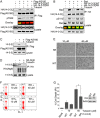
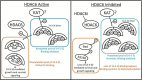
The phospho-binding protein 14-3-3ζ acts as a signaling hub controlling a network of interacting partners and oncogenic pathways. We show here that lysines within the 14-3-3ζ binding pocket and protein-protein interface can be modified by acetylation. The positive charge on two of these lysines, Lys(49) and Lys(120), is critical for coordinating 14-3-3ζ-phosphoprotein interactions. Through screening, we identified HDAC6 as the Lys(49)/Lys(120) deacetylase. Inhibition of HDAC6 blocks 14-3-3ζ interactions with two well described interacting partners, Bad and AS160, which triggers their dephosphorylation at Ser(112) and Thr(642), respectively. Expression of an acetylation-refractory K49R/K120R mutant of 14-3-3ζ rescues both the HDAC6 inhibitor-induced loss of interaction and Ser(112)/Thr(642) phosphorylation. Furthermore, expression of the K49R/K120R mutant of 14-3-3ζ inhibits the cytotoxicity of HDAC6 inhibition. These data demonstrate a novel role for HDAC6 in controlling 14-3-3ζ binding activity.
Keywords: 14-3- Protein; Apoptosis; Cell Signaling; Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6); Metabolic Stress; Non-histone Acetylation; Stress.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Yang X., Cao W., Zhang L., Zhang W., Zhang X., Lin H. (2012) Targeting 14-3-3ζ in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 19, 153–159 - PubMed
-
- Chen S., Synowsky S., Tinti M., MacKintosh C. (2011) The capture of phosphoproteins by 14-3-3 proteins mediates actions of insulin. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 22, 429–436 - PubMed
-
- Cheng J. C., McBrayer S. K., Coarfa C., Dalva-Aydemir S., Gunaratne P. H., Carpten J. D., Keats J. K., Rosen S. T., Shanmugam M. (2013) Expression and phosphorylation of the AS160_v2 splice variant supports GLUT4 activation and the Warburg effect in multiple myeloma. Cancer Metab. 1, 14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garrido P., Osorio F. G., Morán J., Cabello E., Alonso A., Freije J. M., González C. (2015) Loss of GLUT4 induces metabolic reprogramming and impairs viability of breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 230, 191–198 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

