Intertwined regulation of angiogenesis and immunity by myeloid cells
- PMID: 25770923
- PMCID: PMC4393787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2015.02.005
Intertwined regulation of angiogenesis and immunity by myeloid cells
Abstract
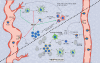
Angiogenesis is a hallmark of cancer because its induction is indispensable to fuel an expanding tumor. The tumor microenvironment contributes to tumor vessel growth, and distinct myeloid cells recruited by the tumor have been shown not only to support angiogenesis but also to foster an immune suppressive environment that supports tumor expansion and progression. Recent findings suggest that the intertwined regulation of angiogenesis and immune modulation can offer therapeutic opportunities for the treatment of cancer. We review the mechanisms by which distinct myeloid cell populations contribute to tumor angiogenesis, discuss current approaches in the clinic that are targeting both angiogenic and immune suppressive pathways, and highlight important areas of future research.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bergers G, Benjamin LE. Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nature reviews. Cancer. 2003;3:401–410. - PubMed
-
- Baluk P, et al. Cellular abnormalities of blood vessels as targets in cancer. Current opinion in genetics & development. 2005;15:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–936. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak HF. Tumors: wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. The New England journal of medicine. 1986;315:1650–1659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

