Mussel adhesive protein provides cohesive matrix for collagen type-1α
- PMID: 25770997
- PMCID: PMC4361793
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.01.033
Mussel adhesive protein provides cohesive matrix for collagen type-1α
Abstract
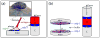
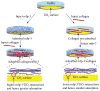
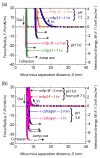
Understanding the interactions between collagen and adhesive mussel foot proteins (mfps) can lead to improved medical and dental adhesives, particularly for collagen-rich tissues. Here we investigated interactions between collagen type-1, the most abundant load-bearing animal protein, and mussel foot protein-3 (mfp-3) using a quartz crystal microbalance and surface forces apparatus (SFA). Both hydrophilic and hydrophobic variants of mfp-3 were exploited to probe the nature of the interaction between the protein and collagen. Our chief findings are: 1) mfp-3 is an effective chaperone for tropocollagen adsorption to TiO2 and mica surfaces; 2) at pH 3, collagen addition between two mfp-3 films (Wc = 5.4 ± 0.2 mJ/m(2)) increased their cohesion by nearly 35%; 3) oxidation of Dopa in mfp-3 by periodate did not abolish the adhesion between collagen and mfp-3 films, and 4) collagen bridging between both hydrophilic and hydrophobic mfp-3 variant films is equally robust, suggesting that hydrophobic interactions play a minor role. Extensive H-bonding, π-cation and electrostatic interactions are more plausible to explain the reversible bridging of mfp-3 films by collagen.
Keywords: Collagen type-1; Mfp-3; Mussel foot proteins; Mylitus californiaus.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Rojkind M, Giambrone MA, Biempica L. Collagen Types in Normal and Cirrhotic Liver. Gastroenterology. 1979;76:710–9. - PubMed
-
- Riechert K, Labs K, Lindenhayn K, Sinha P. Semiquantitative analysis of types I and III collagen from tendons and ligaments in a rabbit model. J Orthop Sci. 2001;6:68–74. - PubMed
-
- Heino J. The collagen family members as cell adhesion proteins. Bioessays. 2007;29:1001–10. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Schneiderman R, Bank RA, Wachtel E, Maroudas A. Mechanical properties of the collagen network in human articular cartilage as measured by osmotic stress technique. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1998;351:207–19. - PubMed
-
- Rodeo SA, Arnoczky SP, Torzilli PA, Hidaka C, Warren RF. Tendon-Healing in a Bone Tunnel - a Biomechanical and Histological Study in the Dog. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75A:1795–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

