Salivary cortisol results obtainable within minutes of sample collection correspond with traditional immunoassays
- PMID: 25773457
- PMCID: PMC4568741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.014
Salivary cortisol results obtainable within minutes of sample collection correspond with traditional immunoassays
Abstract
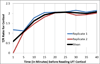
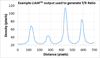
Purpose: Cortisol is frequently assayed as a stress-responsive biomarker which changes over the course of minutes to meet the demands of a person's social context. Salivary cortisol is often used as a noninvasive sampling method that possesses important health implications. A critical barrier to psychobiological research that involves salivary cortisol is a time delay of days to months before cortisol results are obtained via immunoassay, long after the person is no longer proximate to the social context in which they provided the sample. The present study was designed to address this critical barrier through creation of a lateral flow test (LFT) cortisol device capable of measuring salivary cortisol within minutes of sample collection. The LFT is frequently used within commercial point-of-care settings to obtain rapid answers to the presence/absence of a biomarker. The present study extends the LFT into the research domain by presenting performance characteristics of a quantitative LFT that measures salivary cortisol within 20 minutes of sample collection.
Methods: Saliva samples from 29 adults (15 men) were obtained in the morning and afternoon by using Passive Drool and then the Super·SAL Extra Collection Device (hereafter Super·SAL) and later assayed with LFT and a commercially available enzyme immunoassay.
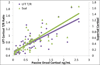
Findings: Results indicate the LFT correlated well with these collection methods (R = 0.872 with Super · SAL, R = 0.739 with Passive Drool, P < 0.0001) and at comparable levels to correspondence of Super · SAL with Passive Drool (R = 0.798, P < 0.0001) which were measured with the same assay.
Implications: These results open an exciting new possibility to integrate this technologic advance into stress research, including knowing and potentially changing the person's social context in a time-sensitive manner. Methodological improvements such as this have the possibility of refining conceptual models of stress reactivity and regulation.
Keywords: collection methods; cortisol; immunoassay; lateral flow technology; stress regulation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier HS Journals, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The first author has no conflicts of interest to declare: EAS does not have a financial stake in the product and sits as a volunteer on the board of advisors of Oasis Diagnostics®.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New techniques for augmenting saliva collection: bacon rules and lozenge drools.Clin Ther. 2015 Mar 1;37(3):515-522. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.015. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25773460 Free PMC article.
-
[Evaluation of new saliva collection device for determination of salivary cotinine, cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone and testosterone concentrations].Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2009 Sep;64(4):811-6. doi: 10.1265/jjh.64.811. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19797850 Japanese.
-
Effectiveness of saliva collection and enzyme-immunoassay for the quantification of cortisol in socially housed baboons.Am J Primatol. 2008 Dec;70(12):1145-51. doi: 10.1002/ajp.20613. Am J Primatol. 2008. PMID: 18785637
-
[Methodological guidelines for the use of salivary cortisol as biological marker of stress].Presse Med. 2003 May 24;32(18):845-51. Presse Med. 2003. PMID: 12870390 Review. French.
-
Psychosocial Influences on Acceptability and Feasibility of Salivary Cortisol Collection From Community Samples of Children.Res Nurs Health. 2016 Dec;39(6):449-462. doi: 10.1002/nur.21744. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Res Nurs Health. 2016. PMID: 27686043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Salivary Cortisol.ACS Omega. 2020 Dec 17;5(51):32890-32898. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03223. eCollection 2020 Dec 29. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33403250 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Biosensors by Means of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) Cortisol Recognition.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;17(4):545. doi: 10.3390/polym17040545. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006210 Free PMC article.
-
Do Parental Hormone Levels Synchronize During the Prenatal and Postpartum Periods? A Systematic Review.Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2024 Sep;27(3):658-676. doi: 10.1007/s10567-024-00474-7. Epub 2024 Apr 14. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38615295 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic exposure to multiple stressors alters the salivary proteome of piglets.PLoS One. 2023 May 26;18(5):e0286455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286455. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37235602 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines Levels and Salivary Microbiome Play A Potential Role in Oral Lichen Planus Diagnosis.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 2;9(1):18137. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54615-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31792433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McEwen BS, Seeman T. Protective and damaging effects of mediators of stress. Elaborating and testing the concepts of allostasis and allostatic load. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;896:30–47. - PubMed
-
- Juster RP, McEwen BS, Lupien SJ. Allostatic load biomarkers of chronic stress and impact on health and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010;35(1):2–16. - PubMed
-
- Lupien SJ, Ouellet-Morin I, Hupbach A, et al. Beyond the stress concept: Allostatic Load--A developmental biological and cognitive perspective. In: Cicchetti D, Cohen D, editors. Developmental Psychopathology. 2nd ed. Vol. 2. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2006. pp. 578–628.
-
- Uno H, Eisele S, Sakai A, et al. Neurotoxicity of glucocorticoids in the primate brain. Horm Behav. 1994;28(4):336–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

