Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into nerve-like cells in vitro after transfection with brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene
- PMID: 25773996
- PMCID: PMC4368845
- DOI: 10.1007/s11626-015-9875-1
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into nerve-like cells in vitro after transfection with brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene
Abstract
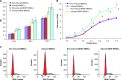
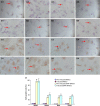
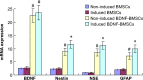
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells can differentiate into a variety of adult cells. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is briefly active during differentiation and induces mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into nerve cells. In this study, we cloned human BDNF to generate a recombinant pcDNA3.1(-)-BDNF vector and transfected the vector into bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. We selected these cells with Geneticin-418 to obtain BDNF-BMSCs, which were induced with retinoic acid to obtain induced BDNF-BMSCs. The transfected cells displayed the typical morphology and surface antigen profile of fibroblasts and were observed to express clusters of differentiation 29, 44, and 90 (observed in matrix and stromal cells), but not clusters of differentiation 31, 34, and 45 (observed in red blood cells and endothelial cells), via flow cytometry. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays showed that transfected bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells secreted more BDNF than non-transfected bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Immunocytochemistry and real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis showed that non-induced BDNF-BMSCs maintained a higher proliferative capacity and expressed higher amounts of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nestin, neuron-specific enolase, and glial fibrillary acid protein than non-transfected bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. An additional increase was observed in the induced BDNF-BMSCs compared to the non-induced BDNF-BMSCs. This expression profile is characteristic of neurocytes. Our data demonstrate that bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transfected with the BDNF gene can differentiate into nerve-like cells in vitro, which may enable the generation of sufficient quantities of nerve-like cells for treatment of neuronal diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of nerve growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor dual gene modification on rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into neuron-like cells in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jan;13(1):49-58. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4553. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26572749 Free PMC article.
-
[Transfection of BDNF gene promotes bone mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into neuron-like cells].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2012 May;37(5):441-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2012.05.002. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2012. PMID: 22659671 Chinese.
-
[Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into nucleus pulposus-like cells transfected by SOX9 eukaryotic expression vector in vitro].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Jul;24(7):811-6. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20695377 Chinese.
-
[Progress of induced osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfected by double-gene].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Dec;28(12):1540-3. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25826903 Review. Chinese.
-
[Research progress on effects of traditional Chinese medicines on proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;39(15):2834-7. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25423818 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effects of TGF-β1 Overexpression on Biological Characteristics of Human Dental Pulp-derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Int J Stem Cells. 2019 Mar 30;12(1):170-182. doi: 10.15283/ijsc18051. Int J Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 30595006 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophin-3 Promotes the Neuronal Differentiation of BMSCs and Improves Cognitive Function in a Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Feb 10;15:629356. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.629356. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33642999 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy: a promising therapeutic target for improving mesenchymal stem cell biological functions.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Feb;476(2):1135-1149. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03978-2. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33196943 Review.
-
Comparison of the Biological Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Bone Marrow and Skin.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3658798. doi: 10.1155/2016/3658798. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27239202 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Nerve Growth Factor and Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Promote Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells to Neural Differentiation.Neurochem Res. 2017 Apr;42(4):1015-1025. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2134-3. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28005222
References
-
- Alves da Silva ML, Martins A, Costa-Pinto AR, Correlo VM, Sol P, Bhattacharya M, Faria S, Reis RL, Neves NM. Chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in chitosan-based scaffolds using a flow-perfusion bioreactor. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(9):722–732. doi: 10.1002/term.372. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

