The mirror illusion: does proprioceptive drift go hand in hand with sense of agency?
- PMID: 25774145
- PMCID: PMC4342885
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00200
The mirror illusion: does proprioceptive drift go hand in hand with sense of agency?
Abstract
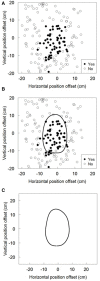
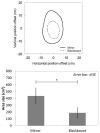
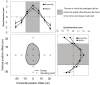
Vection can be regarded as the illusion of "whole-body" position perception. In contrast, the mirror illusion is that of "body-part" position perception. When participants viewed their left hands in a mirror positioned along the midsaggital axis while moving both hands synchronously, they hardly noticed the spatial offset between the hand in the mirror and the obscured real right hand. This illusion encompasses two phenomena: proprioceptive drift and sense of agency. Proprioceptive drift represented a perceptual change in the position of the obscured hand relative to that of the hand in the mirror. Sense of agency referred to the participants' subjective sense of controlling body image as they would their own bodies. We examined the spatial offset between these two phenomena. Participants responded to a two-alternative forced choice (2AFC) question regarding the subjective position of their right hands and questionnaires regarding sense of agency at various positions of the right hand. We analyzed the 2AFC data using a support vector machine and compared its classification result and the questionnaire results. Our data analysis suggested that the two phenomena were observed in concentric space, but the estimated range of the proprioceptive drift was slightly narrower than the range of agency. Although this outcome can be attributed to differences in measurement or analysis, to our knowledge, this is the first report to suggest that proprioceptive drift and sense of agency are concentric and almost overlap.
Keywords: mirror illusion; proprioceptive drift; sense of agency; sense of ownership; vection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Visualization Method for Proprioceptive Drift on a 2D Plane Using Support Vector Machine.J Vis Exp. 2016 Oct 27;(116):53970. doi: 10.3791/53970. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27842352 Free PMC article.
-
Body ownership and agency: task-dependent effects of the virtual hand illusion on proprioceptive drift.Exp Brain Res. 2017 Jan;235(1):121-134. doi: 10.1007/s00221-016-4777-3. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Exp Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 27651139
-
The role of the cerebellum in dynamic changes of the sense of body ownership: a study in patients with cerebellar degeneration.J Cogn Neurosci. 2014 Apr;26(4):712-21. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00522. Epub 2013 Nov 18. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24236765
-
Altered Sense of Body Ownership and Agency in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Its Dissociative Subtype: A Rubber Hand Illusion Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2018 May 1;12:163. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00163. eCollection 2018. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29765311 Free PMC article.
-
Agency elicits body-ownership: proprioceptive drift toward a synchronously acting external proxy.Exp Brain Res. 2016 May;234(5):1163-74. doi: 10.1007/s00221-015-4231-y. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Exp Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 25716612
Cited by
-
Changes in perceived peripersonal space following the rubber hand illusion.Sci Rep. 2023 May 12;13(1):7713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34620-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37173340 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication strategies for chiral self-assembly surface.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Mar 16;191(4):202. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06278-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38492117 Review.
-
Visualization Method for Proprioceptive Drift on a 2D Plane Using Support Vector Machine.J Vis Exp. 2016 Oct 27;(116):53970. doi: 10.3791/53970. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27842352 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanotactile Sensory Feedback Improves Embodiment of a Prosthetic Hand During Active Use.Front Neurosci. 2020 Mar 26;14:263. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00263. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32273838 Free PMC article.
-
Body ownership and the absence of touch: approaching the rubber hand inside and outside peri-hand space.Exp Brain Res. 2018 Dec;236(12):3251-3265. doi: 10.1007/s00221-018-5361-9. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Exp Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 30220004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bishop C. M. (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. New York, NY: Springer.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

