Pneumomediastinum
- PMID: 25774307
- PMCID: PMC4332083
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.01.11
Pneumomediastinum
Abstract
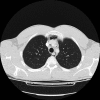
Pneumomediastinum is a condition in which air is present in the mediastinum. This condition can result from physical trauma or other situations that lead to air escaping from the lungs, airways or bowel into the chest cavity. Pneumomediastinum is a rare situation and occurs when air leaks into the mediastinum. The diagnosis can be confirmed via chest X-ray or CT scanning of the thorax. The main symptom is usually severe central chest pain. Other symptoms include laboured breathing, voice distortion (as with helium) and subcutaneous emphysema, specifically affecting the face, neck, and chest. Pneumomediastinum can also be characterized by the shortness of breath that is typical of a respiratory system problem. It is often recognized on auscultation by a "crunching" sound timed with the cardiac cycle (Hamman's crunch). Pnemomediastinum may also present with symptoms mimicking cardiac tamponade as a result of the increased intrapulmonary pressure on venous flow to the heart. The tissues in the mediastinum will slowly resorb the air in the cavity so most pneumomediastinums are treated conservatively.
Keywords: Pneumothorax; pneumomediastinum; puncture; trauma.
Figures





References
-
- Agut A, Talavera J, Buendia A, et al. Imaging diagnosis-spontaneous pneumomediastinum secondary to primary pulmonary pathology in a dalmatian dog. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2014. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
-
- Kobashi Y, Okimoto N, Matsushima T, et al. Comparative study of mediastinal emphysema as determined by etiology. Intern Med 2002;41:277-82. - PubMed
-
- Chiu CY, Wong KS, Yao TC, et al. Asthmatic versus non-asthmatic spontaneous pneumomediastinum in children. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 2005;23:19-22. - PubMed
-
- Macia I, Moya J, Ramos R, et al. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: 41 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2007;31:1110-4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
