Actin dynamics tune the integrated stress response by regulating eukaryotic initiation factor 2α dephosphorylation
- PMID: 25774599
- PMCID: PMC4394351
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.04872
Actin dynamics tune the integrated stress response by regulating eukaryotic initiation factor 2α dephosphorylation
Abstract
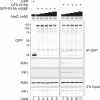
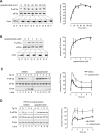
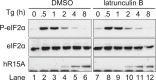
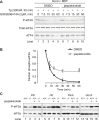
Four stress-sensing kinases phosphorylate the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2α) to activate the integrated stress response (ISR). In animals, the ISR is antagonised by selective eIF2α phosphatases comprising a catalytic protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) subunit in complex with a PPP1R15-type regulatory subunit. An unbiased search for additional conserved components of the PPP1R15-PP1 phosphatase identified monomeric G-actin. Like PP1, G-actin associated with the functional core of PPP1R15 family members and G-actin depletion, by the marine toxin jasplakinolide, destabilised the endogenous PPP1R15A-PP1 complex. The abundance of the ternary PPP1R15-PP1-G-actin complex was responsive to global changes in the polymeric status of actin, as was its eIF2α-directed phosphatase activity, while localised G-actin depletion at sites enriched for PPP1R15 enhanced eIF2α phosphorylation and the downstream ISR. G-actin's role as a stabilizer of the PPP1R15-containing holophosphatase provides a mechanism for integrating signals regulating actin dynamics with stresses that trigger the ISR.
Keywords: CReP; D. melanogaster; GADD34; PPP1R15A; PPP1R15B; actin; biochemistry; cell biology; human; integrated stress response; mouse.
Conflict of interest statement
DR: Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures







References
-
- Axten JM, Medina JR, Feng Y, Shu A, Romeril SP, Grant SW, Li WH, Heerding DA, Minthorn E, Mencken T, Atkins C, Liu Q, Rabindran S, Kumar R, Hong X, Goetz A, Stanley T, Taylor JD, Sigethy SD, Tomberlin GH, Hassell AM, Kahler KM, \Shewchuk LM, Gampe RT. Discovery of 7-methyl-5-(1-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetyl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-5-xyl)-7H-p yrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (GSK2606414), a potent and selective first-in-class inhibitor of protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2012;55:7193–7207. doi: 10.1021/jm300713s. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brush MH, Weiser DC, Shenolikar S. Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 targets protein phosphatase 1alpha to the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes dephosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2003;23:1292–1303. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1292-1303.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clemens M. Protein kinases that phosphorylate eIF2 and eIF2B, their role in eukaryotic cell translational control. In: Hershey J, Mathews M, Sonenberg N, editors. Translational control. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1996. pp. 139–172.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

