G-actin provides substrate-specificity to eukaryotic initiation factor 2α holophosphatases
- PMID: 25774600
- PMCID: PMC4394352
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.04871
G-actin provides substrate-specificity to eukaryotic initiation factor 2α holophosphatases
Abstract
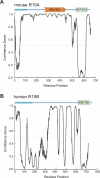
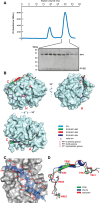
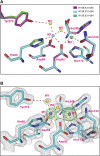
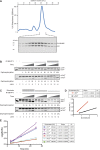
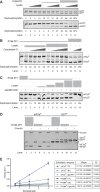
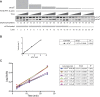
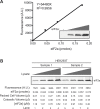
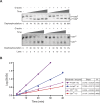
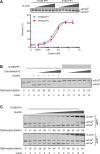
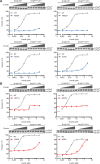
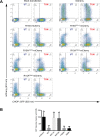
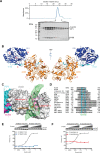
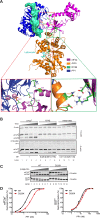
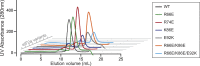
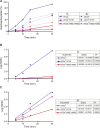
Dephosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2a (eIF2a) restores protein synthesis at the waning of stress responses and requires a PP1 catalytic subunit and a regulatory subunit, PPP1R15A/GADD34 or PPP1R15B/CReP. Surprisingly, PPP1R15-PP1 binary complexes reconstituted in vitro lacked substrate selectivity. However, selectivity was restored by crude cell lysate or purified G-actin, which joined PPP1R15-PP1 to form a stable ternary complex. In crystal structures of the non-selective PPP1R15B-PP1G complex, the functional core of PPP1R15 made multiple surface contacts with PP1G, but at a distance from the active site, whereas in the substrate-selective ternary complex, actin contributes to one face of a platform encompassing the active site. Computational docking of the N-terminal lobe of eIF2a at this platform placed phosphorylated serine 51 near the active site. Mutagenesis of predicted surface-contacting residues enfeebled dephosphorylation, suggesting that avidity for the substrate plays an important role in imparting specificity on the PPP1R15B-PP1G-actin ternary complex.
Keywords: E. coli; biochemistry; biophysics; cell lines; human; mouse; rabbit; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
DR: Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
-
- Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Moriarty NW, Mustyakimov M, Terwilliger TC, Urzhumtsev A, Zwart PH, Adams PD. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallographica Section D, Biological Crystallography. 2012;68:352–367. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912001308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Street AJ, Cohen P, Cohen PT. Inhibitor-2 functions like a chaperone to fold three expressed isoforms of mammalian protein phosphatase-1 into a conformation with the specificity and regulatory properties of the native enzyme. European Journal of Biochemistry. 1993;213:1055–1066. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17853.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brush MH, Weiser DC, Shenolikar S. Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 targets protein phosphatase 1 alpha to the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes dephosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2003;23:1292–1303. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1292-1303.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

