Enhanced functions of peripheral γδ T cells in chronic hepatitis B infection during interferon α treatment in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 25774808
- PMCID: PMC4361562
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120086
Enhanced functions of peripheral γδ T cells in chronic hepatitis B infection during interferon α treatment in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
Background: γδ T cells play an important role in infectious, autoimmune, or neoplastic diseases. Here, a study was conducted to investigate the dynamic changes in phenotype and function of peripheral γδ T cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) during pegylated-interferon (pegIFN)-α treatment, and to explore their roles in IFN-α therapy.
Methods: Total 15 CHB patients with pegIFN-α therapy and 6 healthy controls (HC) were enrolled in this study. Flow cytometry was used for the study of frequency of peripheral γδ T cells, subtypes, effector or memory γδ T cells, and also the IFN-γ+, TNF-α+, CD107a+ or Granzyme B+ γδ T cells in 10 patients at week 0, 4, 8, 12, 24, 36 and 48 of treatment. Another 5 CHB patients and 6 HC were recruited for the γδ T cell isolation, and gene expression in γδ T cells was evaluated before or after IFN-α treatment in vitro.
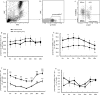
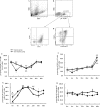
Results: Although γδT cells decreased in CHB patients during pegIFN-α therapy, their capacities to produce TNF-α and to express CD107a were enhanced. More effector γδT cells (CD27-CD45RA+) were found in the response group than in non-response group. Furthermore, IFN-α boosted the expression of Mx2 and cytokine genes in γδT cells from CHB patients in vitro.
Conclusion: IFN-α could enhance the cytokine production or cytotoxicity potential of γδT cells in vivo and in vitro. The enhanced function of γδT cells might contribute to the effect of IFN-α treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pegylated interferon α enhances recovery of memory T cells in e antigen positive chronic hepatitis B patients.Virol J. 2012 Nov 16;9:274. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-274. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 23158844 Free PMC article.
-
A possible role for NKT-like cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B during telbivudine treatment.Immunol Lett. 2014 Jul;160(1):65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.03.013. Epub 2014 Apr 6. Immunol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24718278
-
Enhanced peripheral γδT cells cytotoxicity potential in patients with HBV-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure might contribute to the disease progression.J Clin Immunol. 2012 Aug;32(4):877-85. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9678-z. Epub 2012 Mar 14. J Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22415432
-
Immune-modulators to combat hepatitis B virus infection: From IFN-α to novel investigational immunotherapeutic strategies.Antiviral Res. 2015 Oct;122:69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 26275801 Review.
-
Interferon and Hepatitis B: Current and Future Perspectives.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 7;12:733364. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.733364. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34557195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of γδ T Cells in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720966980. doi: 10.1177/0963689720966980. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33073597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immunity and early liver inflammation.Front Immunol. 2023 May 2;14:1175147. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1175147. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37205101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of γδT cells in liver diseases and its relationship with intestinal microbiota.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 May 28;26(20):2559-2569. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i20.2559. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32523311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Contribution of Human Herpes Viruses to γδ T Cell Mobilisation in Co-Infections.Viruses. 2021 Nov 26;13(12):2372. doi: 10.3390/v13122372. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34960641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse Subsets of γδT Cells and Their Specific Functions Across Liver Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 19;26(6):2778. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062778. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parmar S, Platanias LC. Interferons: mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Curr Opin Oncol. 2003;15: 431–439. - PubMed
-
- Craxi A, Cooksley WG. Pegylated interferons for chronic hepatitis B. Antiviral Res. 2003; 60: 87–89. - PubMed
-
- Belloni L, Allweiss L, Guerrieri F, Pediconi N, Volz T, Pollicino T, et al. IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122: 529–537. 10.1172/JCI58847 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

