IL-24 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by disrupting the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling axis
- PMID: 25775124
- PMCID: PMC4361489
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122439
IL-24 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by disrupting the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling axis
Abstract
Background: The stromal cell derived factor (SDF)-1/chemokine receptor (CXCR)-4 signaling pathway plays a key role in lung cancer metastasis and is molecular target for therapy. In the present study we investigated whether interleukin (IL)-24 can inhibit the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis and suppress lung cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro. Further, the efficacy of IL-24 in combination with CXCR4 antagonists was investigated.
Methods: Human H1299, A549, H460 and HCC827 lung cancer cell lines were used in the present study. The H1299 lung cancer cell line was stably transfected with doxycycline-inducible plasmid expression vector carrying the human IL-24 cDNA and used in the present study to determine the inhibitory effects of IL-24 on SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. H1299 and A549 cell lines were used in transient transfection studies. The inhibitory effects of IL-24 on SDF1/CXCR4 and its downstream targets were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR, western blot, luciferase reporter assay, flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry. Functional studies included cell migration and invasion assays.
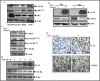
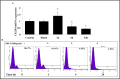
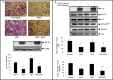
Principal findings: Endogenous CXCR4 protein expression levels varied among the four human lung cancer cell lines. Doxycycline-induced IL-24 expression in the H1299-IL24 cell line resulted in reduced CXCR4 mRNA and protein expression. IL-24 post-transcriptionally regulated CXCR4 mRNA expression by decreasing the half-life of CXCR4 mRNA (>40%). Functional studies showed IL-24 inhibited tumor cell migration and invasion concomitant with reduction in CXCR4 and its downstream targets (pAKTS473, pmTORS2448, pPRAS40T246 and HIF-1α). Additionally, IL-24 inhibited tumor cell migration both in the presence and absence of the CXCR4 agonist, SDF-1. Finally, IL-24 when combined with CXCR4 inhibitors (AMD3100, SJA5) or with CXCR4 siRNA demonstrated enhanced inhibitory activity on tumor cell migration.
Conclusions: IL-24 disrupts the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway and inhibits lung tumor cell migration and invasion. Additionally, IL-24, when combined with CXCR4 inhibitors exhibited enhanced anti-metastatic activity and is an attractive therapeutic strategy for lung metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Upregulation of CXCR4 is functionally crucial for maintenance of stemness in drug-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells.Oncogene. 2013 Jan 10;32(2):209-21. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.37. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22370645
-
Hesperidin suppresses the migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting the SDF-1/CXCR-4 pathway.Life Sci. 2018 May 15;201:111-120. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.046. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29604270
-
AMD3100 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell invasion, and metastasis in the liver and the lung through blocking the SDF-1α/CXCR4 signaling pathway in prostate cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jul;234(7):11746-11759. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27831. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30537000
-
Potential of CXCR4 antagonists for the treatment of metastatic lung cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011 Apr;11(4):621-30. doi: 10.1586/era.11.11. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21504328 Review.
-
Targeting CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis in Tumor Immunotherapy.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(17):3026-3041. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170830111531. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 28875842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rigid Macrocycle Metal Complexes as CXCR4 Chemokine Receptor Antagonists: Influence of Ring Size.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 28;16(8):1000. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081000. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204345 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Conditioned Medium Modulates Functional and Phenotypic Properties of Human Decidua Parietalis Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019 Nov 1;16(6):615-630. doi: 10.1007/s13770-019-00207-w. eCollection 2019 Dec. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019. PMID: 31824824 Free PMC article.
-
Regorafenib sensitizes human breast cancer cells to radiation by inhibiting multiple kinases and inducing DNA damage.Int J Radiat Biol. 2021;97(8):1109-1120. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1730012. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Int J Radiat Biol. 2021. PMID: 32052681 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Action and Applications of Interleukin 24 in Immunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 2;17(6):869. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060869. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27271601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Bridge too Far? Comparison of Transition Metal Complexes of Dibenzyltetraazamacrocycles with and without Ethylene Cross-Bridges: X-ray Crystal Structures, Kinetic Stability, and Electronic Properties.Molecules. 2023 Jan 16;28(2):895. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020895. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Lutz M, Belperio JA, Keane MP, Strieter RM. The stromal derived factor-1/CXCL12-CXC chemokine receptor 4 biological axis in non-small cell lung cancer metastases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 167: 1676–1686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
