The 1.7 Å X-ray crystal structure of the porcine factor VIII C2 domain and binding analysis to anti-human C2 domain antibodies and phospholipid surfaces
- PMID: 25775247
- PMCID: PMC4361576
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122447
The 1.7 Å X-ray crystal structure of the porcine factor VIII C2 domain and binding analysis to anti-human C2 domain antibodies and phospholipid surfaces
Abstract
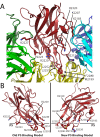
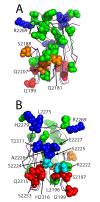
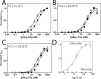
The factor VIII C2 domain is essential for binding to activated platelet surfaces as well as the cofactor activity of factor VIII in blood coagulation. Inhibitory antibodies against the C2 domain commonly develop following factor VIII replacement therapy for hemophilia A patients, or they may spontaneously arise in cases of acquired hemophilia. Porcine factor VIII is an effective therapeutic for hemophilia patients with inhibitor due to its low cross-reactivity; however, the molecular basis for this behavior is poorly understood. In this study, the X-ray crystal structure of the porcine factor VIII C2 domain was determined, and superposition of the human and porcine C2 domains demonstrates that most surface-exposed differences cluster on the face harboring the "non-classical" antibody epitopes. Furthermore, antibody-binding results illustrate that the "classical" 3E6 antibody can bind both the human and porcine C2 domains, although the inhibitory titer to human factor VIII is 41 Bethesda Units (BU)/mg IgG versus 0.8 BU/mg IgG to porcine factor VIII, while the non-classical G99 antibody does not bind to the porcine C2 domain nor inhibit porcine factor VIII activity. Further structural analysis of differences between the electrostatic surface potentials suggest that the C2 domain binds to the negatively charged phospholipid surfaces of activated platelets primarily through the 3E6 epitope region. In contrast, the G99 face, which contains residue 2227, should be distal to the membrane surface. Phospholipid binding assays indicate that both porcine and human factor VIII C2 domains bind with comparable affinities, and the human K2227A and K2227E mutants bind to phospholipid surfaces with similar affinities as well. Lastly, the G99 IgG bound to PS-immobilized factor VIII C2 domain with an apparent dissociation constant of 15.5 nM, whereas 3E6 antibody binding to PS-bound C2 domain was not observed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structure of the Human Factor VIII C2 Domain in Complex with the 3E6 Inhibitory Antibody.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 24;5:17216. doi: 10.1038/srep17216. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26598467 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the factor VIII C2 domain in a ternary complex with 2 inhibitor antibodies reveals classical and nonclassical epitopes.Blood. 2013 Dec 19;122(26):4270-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-519124. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24085769 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of Blood Coagulation Factor VIII in Complex With an Anti-C2 Domain Non-Classical, Pathogenic Antibody Inhibitor.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 10;12:697602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.697602. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34177966 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into binding interfaces of coagulation factors V and VIII and their homologues lessons from high resolution crystal structures.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002 Jun;3(3):313-39. doi: 10.2174/1389203023380639. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002. PMID: 12188899 Review.
-
Properties of anti-factor VIII inhibitor antibodies in hemophilia A patients.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000;26(2):137-42. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-9815. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000. PMID: 10919405 Review.
Cited by
-
Flow-Cytometry Platform for Intracellular Detection of FVIII in Blood Cells: A New Tool to Assess Gene Therapy Efficiency for Hemophilia A.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2019 Nov 15;17:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2019.11.003. eCollection 2020 Jun 12. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2019. PMID: 31886317 Free PMC article.
-
SAXS analysis of the intrinsic tenase complex bound to a lipid nanodisc highlights intermolecular contacts between factors VIIIa/IXa.Blood Adv. 2022 Jun 14;6(11):3240-3254. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005874. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35255502 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Human Factor VIII C2 Domain in Complex with the 3E6 Inhibitory Antibody.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 24;5:17216. doi: 10.1038/srep17216. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26598467 Free PMC article.
-
Stable binding to phosphatidylserine-containing membranes requires conserved arginine residues in tandem C domains of blood coagulation factor VIII.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Oct 26;9:1040106. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1040106. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36387287 Free PMC article.
-
The 3.2 Å structure of a bioengineered variant of blood coagulation factor VIII indicates two conformations of the C2 domain.J Thromb Haemost. 2020 Jan;18(1):57-69. doi: 10.1111/jth.14621. Epub 2019 Sep 8. J Thromb Haemost. 2020. PMID: 31454152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoots WK. The future of plasma-derived clotting factor concentrates. Haemophilia: the official journal of the World Federation of Hemophilia. 2001;7 Suppl 1:4–9. - PubMed
-
- Mauser-Bunschoten EP, van der Bom JG, Bongers M, Twijnstra M, Roosendaal G, Fischer K, et al. Purity of factor VIII product and incidence of inhibitors in previously untreated patients with haemophilia A. Haemophilia: the official journal of the World Federation of Hemophilia. 2001;7(4):364–8. - PubMed
-
- Scharrer I, Bray GL, Neutzling O. Incidence of inhibitors in haemophilia A patients—a review of recent studies of recombinant and plasma-derived factor VIII concentrates. Haemophilia: the official journal of the World Federation of Hemophilia. 1999;5(3):145–54. - PubMed
-
- Bray GL, Gomperts ED, Courter S, Gruppo R, Gordon EM, Manco-Johnson M, et al. A multicenter study of recombinant factor VIII (recombinate): safety, efficacy, and inhibitor risk in previously untreated patients with hemophilia A. The Recombinate Study Group. Blood. 1994;83(9):2428–35. - PubMed
-
- Kreuz W, Ettingshausen CE, Zyschka A, Oldenburg J, Saguer IM, Ehrenforth S, et al. Inhibitor development in previously untreated patients with hemophilia A: a prospective long-term follow-up comparing plasma-derived and recombinant products. Seminars in thrombosis and hemostasis. 2002;28(3):285–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

