Platelet recruitment promotes keratocyte repopulation following corneal epithelial abrasion in the mouse
- PMID: 25775402
- PMCID: PMC4361664
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118950
Platelet recruitment promotes keratocyte repopulation following corneal epithelial abrasion in the mouse
Abstract
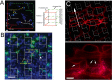
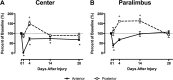
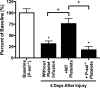
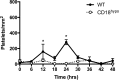
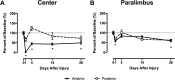
Corneal abrasion not only damages the epithelium but also induces stromal keratocyte death at the site of injury. While a coordinated cascade of inflammatory cell recruitment facilitates epithelial restoration, it is unclear if this cascade is necessary for keratocyte recovery. Since platelet and neutrophil (PMN) recruitment after corneal abrasion is beneficial to epithelial wound healing, we wanted to determine if these cells play a role in regulating keratocyte repopulation after epithelial abrasion. A 2 mm diameter central epithelial region was removed from the corneas of C57BL/6 wildtype (WT), P-selectin deficient (P-sel-/-), and CD18 hypomorphic (CD18hypo) mice using the Algerbrush II. Corneas were studied at 6h intervals out to 48h post-injury to evaluate platelet and PMN cell numbers; additional corneas were studied at 1, 4, 14, and 28 days post injury to evaluate keratocyte numbers. In WT mice, epithelial abrasion induced a loss of anterior central keratocytes and keratocyte recovery was rapid and incomplete, reaching ~70% of uninjured baseline values by 4 days post-injury but no further improvement at 28 days post-injury. Consistent with a beneficial role for platelets and PMNs in wound healing, keratocyte recovery was significantly depressed at 4 days post-injury (~30% of uninjured baseline) in P-sel-/- mice, which are known to have impaired platelet and PMN recruitment after corneal abrasion. Passive transfer of platelets from WT, but not P-sel-/-, into P-sel-/- mice prior to injury restored anterior central keratocyte numbers at 4 days post-injury to P-sel-/- uninjured baseline levels. While PMN infiltration in injured CD18hypo mice was similar to injured WT mice, platelet recruitment was markedly decreased and anterior central keratocyte recovery was significantly reduced (~50% of baseline) at 4-28 days post-injury. Collectively, the data suggest platelets and platelet P-selectin are critical for efficient keratocyte recovery after corneal epithelial abrasion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
ICAM-1 mediates surface contact between neutrophils and keratocytes following corneal epithelial abrasion in the mouse.Exp Eye Res. 2010 Nov;91(5):676-84. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.08.007. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Exp Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20713042 Free PMC article.
-
IL-20 promotes epithelial healing of the injured mouse cornea.Exp Eye Res. 2017 Jan;154:22-29. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27818315 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet response to corneal abrasion is necessary for acute inflammation and efficient re-epithelialization.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Nov;47(11):4794-802. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0381. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 17065490
-
The corneal fibrosis response to epithelial-stromal injury.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jan;142:110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.09.012. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26675407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injury and defective regeneration of the epithelial basement membrane in corneal fibrosis: A paradigm for fibrosis in other organs?Matrix Biol. 2017 Dec;64:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 28625845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regenerative Therapy for Corneal Scarring Disorders.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 14;12(3):649. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030649. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in microfluidic passive separation to enable purification of platelets for transfusion.Biomicrofluidics. 2024 Dec 17;18(6):061504. doi: 10.1063/5.0226060. eCollection 2024 Dec. Biomicrofluidics. 2024. PMID: 39713738 Review.
-
Platelet and Erythrocyte Extravasation across Inflamed Corneal Venules Depend on CD18, Neutrophils, and Mast Cell Degranulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 8;22(14):7360. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147360. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298979 Free PMC article.
-
High fat diet induced gut dysbiosis alters corneal epithelial injury response in mice.Ocul Surf. 2022 Jan;23:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2021.11.006. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Ocul Surf. 2022. PMID: 34808360 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Free Biological Approach for Corneal Stromal Wound Healing.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 28;12:671405. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.671405. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34122095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Helena MC, Baerveldt F, Kim WJ, Wilson SE. Keratocyte apoptosis after corneal surgery. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 1998;39: 276–283. - PubMed
-
- Mohan RR, Hutcheon AEK, Choi R, Hong J, Lee J, Mohan RR, et al. Apoptosis, necrosis, proliferation, and myofibroblast generation in the stroma following LASIK and PRK. Exp Eye Res. 2003;76: 71–87. - PubMed
-
- Jester JV, Moller-Pedersen T, Huang J, Sax CM, Kays WT, Cavangh HD, et al. The cellular basis of corneal transparency: evidence for 'corneal crystallins'. Journal of Cell Science. 1999;112 (Pt 5): 613–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

