RNABP COGEST: a resource for investigating functional RNAs
- PMID: 25776022
- PMCID: PMC4360618
- DOI: 10.1093/database/bav011
RNABP COGEST: a resource for investigating functional RNAs
Abstract
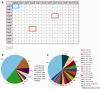
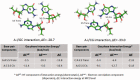
Structural bioinformatics of RNA has evolved mainly in response to the rapidly accumulating evidence that non-(protein)-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) play critical roles in gene regulation and development. The structures and functions of most ncRNAs are however still unknown. Most of the available RNA structural databases rely heavily on known 3D structures, and contextually correlate base pairing geometry with actual 3D RNA structures. None of the databases provide any direct information about stabilization energies. However, the intrinsic interaction energies of constituent base pairs can provide significant insights into their roles in the overall dynamics of RNA motifs and structures. Quantum mechanical (QM) computations provide the only approach toward their accurate quantification and characterization. 'RNA Base Pair Count, Geometry and Stability' (http://bioinf.iiit.ac.in/RNABPCOGEST) brings together information, extracted from literature data, regarding occurrence frequency, experimental and quantum chemically optimized geometries, and computed interaction energies, for non-canonical base pairs observed in a non-redundant dataset of functional RNA structures. The database is designed to enable the QM community, on the one hand, to identify appropriate biologically relevant model systems and also enable the biology community to easily sift through diverse computational results to gain theoretical insights which could promote hypothesis driven biological research.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Bass B.L., Cech T.R. (1984) Specific interaction between the self-splicing RNA of Tetrahymena and its guanosine substrate: implications for biological catalysis by RNA. Nature, 308, 820–826. - PubMed
-
- Tabara H., Sarkissian M., Kelly W.G., et al. . (1999) The rde-1 gene, RNA interference, and transposon silencing in C. elegans. Cell, 99, 123–132. - PubMed
-
- Carter A.P., Clemons W.M., Brodersen D.E., et al. . (2000) Functional insights from the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interactions with antibiotics. Nature, 407, 340–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

