H-ras distribution and signaling in plasma membrane microdomains are regulated by acylation and deacylation events
- PMID: 25776558
- PMCID: PMC4420920
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01398-14
H-ras distribution and signaling in plasma membrane microdomains are regulated by acylation and deacylation events
Erratum in
-
Correction for Agudo-Ibáñez et al., "H-Ras Distribution and Signaling in Plasma Membrane Microdomains Are Regulated by Acylation and Deacylation Events".Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Aug 15;38(17):e00335-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00335-18. Print 2018 Sep 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30111615 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
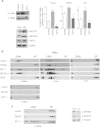
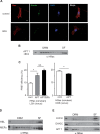
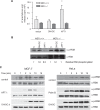
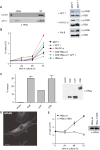
H-Ras must adhere to the plasma membrane to be functional. This is accomplished by posttranslational modifications, including palmitoylation, a reversible process whereby H-Ras traffics between the plasma membrane and the Golgi complex. At the plasma membrane, H-Ras has been proposed to occupy distinct sublocations, depending on its activation status: lipid rafts/detergent-resistant membrane fractions when bound to GDP, diffusing to disordered membrane/soluble fractions in response to GTP loading. Herein, we demonstrate that H-Ras sublocalization is dictated by its degree of palmitoylation in a cell type-specific manner. Whereas H-Ras localizes to detergent-resistant membrane fractions in cells with low palmitoylation activity, it locates to soluble membrane fractions in lineages where it is highly palmitoylated. Interestingly, in both cases GTP loading results in H-Ras diffusing away from its original sublocalization. Moreover, tilting the equilibrium between palmitoylation and depalmitoylation processes can substantially alter H-Ras segregation and, subsequently, its biochemical and biological functions. Thus, the palmitoylation/depalmitoylation balance not only regulates H-Ras cycling between endomembranes and the plasma membrane but also serves as a key orchestrator of H-Ras lateral diffusion between different types of plasma membrane and thereby of H-Ras signaling.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


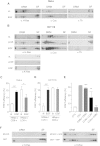
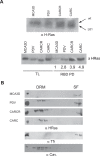
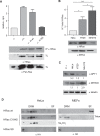
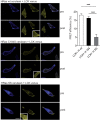

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
