Heat-Stable Dry Powder Oxytocin Formulations for Delivery by Oral Inhalation
- PMID: 25776985
- PMCID: PMC4666249
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-015-0314-0
Heat-Stable Dry Powder Oxytocin Formulations for Delivery by Oral Inhalation
Abstract
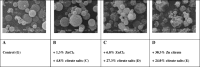
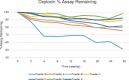
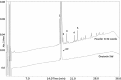
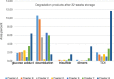
In this work, heat stable dry powders of oxytocin (OT) suitable for delivery by oral inhalation were prepared. The OT dry powders were prepared by spray drying using excipients chosen to promote OT stability including trehalose, isoleucine, polyvinylpyrrolidone, citrate (sodium citrate and citric acid), and zinc salts (zinc chloride and zinc citrate). Characterization by laser diffraction indicated that the OT dry powders had a median particle size of 2 μm, making them suitable for delivery by inhalation. Aerodynamic performance upon discharge from proprietary dry powder inhalers was evaluated by Andersen cascade impaction (ACI) and in an anatomically correct airway (ACA) model, and confirmed that the powders had excellent aerodynamic performance, with respirable fractions up to 77% (ACI, 30 L/min). Physicochemical characterization demonstrated that the powders were amorphous (X-ray diffraction) with high glass transition temperature (modulated differential scanning calorimetry, MDSC), suggesting the potential for stabilization of the OT in a glassy amorphous matrix. OT assay and impurity profile were conducted by reverse phase HPLC and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) after storage up to 32 weeks at 40°C/75%RH. Analysis demonstrated that OT dry powders containing a mixture of citrate and zinc salts retained more than 90% of initial assay after 32 weeks storage and showed significant reduction in dimers and trisulfide formation (up to threefold reduction compared to control).
Keywords: dry powder; oral inhalation; oxytocin; peptide delivery; postpartum hemorrhage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physicochemical stability and aerosolization performance of dry powder inhalation system containing ciprofloxacin hydrochloride.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jan 30;148:73-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Sep 22. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 28965047
-
L-Leucine as an excipient against moisture on in vitro aerosolization performances of highly hygroscopic spray-dried powders.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016 May;102:132-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.02.010. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016. PMID: 26970252
-
Protection of hydrophobic amino acids against moisture-induced deterioration in the aerosolization performance of highly hygroscopic spray-dried powders.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017 Oct;119:224-234. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.06.023. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017. PMID: 28655664
-
Overcoming challenges for development of amorphous powders for inhalation.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Nov;17(11):1583-1595. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1813105. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32811193 Review.
-
Spray-Dried Inhalable Powder Formulations of Therapeutic Proteins and Peptides.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 Jun 18;22(5):185. doi: 10.1208/s12249-021-02043-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 34143327 Review.
Cited by
-
Cost-effectiveness of inhaled oxytocin for prevention of postpartum haemorrhage: a modelling study applied to two high burden settings.BMC Med. 2020 Jul 28;18(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01658-y. BMC Med. 2020. PMID: 32718336 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Single Doses of Oxytocin Administered via an Inhaled Route in Healthy Females: Randomized, Single-blind, Phase 1 Study.EBioMedicine. 2017 Aug;22:249-255. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.07.020. Epub 2017 Jul 22. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 28781129 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rapid Absorption of Dry-Powder Intranasal Oxytocin.Pharm Res. 2016 Aug;33(8):1936-44. doi: 10.1007/s11095-016-1929-x. Epub 2016 May 18. Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 27194003
-
The use of hydrophobic amino acids in protecting spray dried trehalose formulations against moisture-induced changes.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019 Nov;144:139-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.09.014. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019. PMID: 31536784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dept. of Reproductive Health and Research, WHO WHO recommendations for the prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage; 2012.
-
- Hogerzeil HV, Walker GJA, de Goeje MJ. Stability of injectable oxytocics in tropical climates. WHOreportWHO/DAP/93.6;1993.
-
- Groot ANJA, Vree TB, Hogerzeil HV, Walker GJA. Stability of oral oxytocics in tropical climates: Results of simulation studies on oral ergometrine, oral ethylergometrine, buccal oxytocin and buccal desamino-oxytocin. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1997.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

