Causal Interactions Within a Frontal-Cingulate-Parietal Network During Cognitive Control: Convergent Evidence from a Multisite-Multitask Investigation
- PMID: 25778346
- PMCID: PMC4830290
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhv046
Causal Interactions Within a Frontal-Cingulate-Parietal Network During Cognitive Control: Convergent Evidence from a Multisite-Multitask Investigation
Abstract
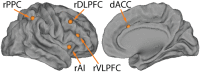
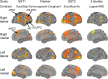
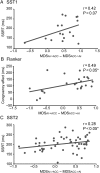
Cognitive control plays an important role in goal-directed behavior, but dynamic brain mechanisms underlying it are poorly understood. Here, using multisite fMRI data from over 100 participants, we investigate causal interactions in three cognitive control tasks within a core Frontal-Cingulate-Parietal network. We found significant causal influences from anterior insula (AI) to dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) in all three tasks. The AI exhibited greater net causal outflow than any other node in the network. Importantly, a similar pattern of causal interactions was uncovered by two different computational methods for causal analysis. Furthermore, the strength of causal interaction from AI to dACC was greater on high, compared with low, cognitive control trials and was significantly correlated with individual differences in cognitive control abilities. These results emphasize the importance of the AI in cognitive control and highlight its role as a causal hub in the Frontal-Cingulate-Parietal network. Our results further suggest that causal signaling between the AI and dACC plays a fundamental role in implementing cognitive control and are consistent with a two-stage cognitive control model in which the AI first detects events requiring greater access to cognitive control resources and then signals the dACC to execute load-specific cognitive control processes.
Keywords: brain network; connectivity; fMRI; human; temporal dependence.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Allman JM, Tetreault NA, Hakeem AY, Manaye KF, Semendeferi K, Erwin JM, Park S, Goubert V, Hof PR. 2010. The von Economo neurons in frontoinsular and anterior cingulate cortex in great apes and humans. Brain Struct Funct. 214:495–517. - PubMed
-
- Andersen RA, Cui H. 2009. Intention, action planning, and decision making in parietal-frontal circuits. Neuron. 63:568–583. - PubMed
-
- Botvinick MM, Cohen JD, Carter CS. 2004. Conflict monitoring and anterior cingulate cortex: an update. Trends Cogn Sci. 8:539–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

