Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4) acts as an inhibitor of ID-1, -2 and -3 and promotes basic helix loop helix (bHLH) E47 DNA binding and transcriptional activity
- PMID: 25778840
- PMCID: PMC4402281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.03.006
Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4) acts as an inhibitor of ID-1, -2 and -3 and promotes basic helix loop helix (bHLH) E47 DNA binding and transcriptional activity
Abstract
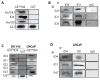
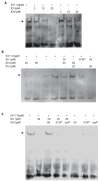
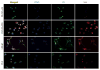
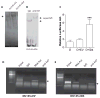
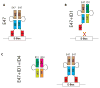
The four known ID proteins (ID1-4, Inhibitor of Differentiation) share a homologous helix loop helix (HLH) domain and act as dominant negative regulators of basic-HLH transcription factors. ID proteins also interact with many non-bHLH proteins in complex networks. The expression of ID proteins is increasingly observed in many cancers. Whereas ID-1, ID-2 and ID-3, are generally considered as tumor promoters, ID4 on the contrary has emerged as a tumor suppressor. In this study we demonstrate that ID4 heterodimerizes with ID-1, -2 and -3 and promote bHLH DNA binding, essentially acting as an inhibitor of inhibitors of differentiation proteins. Interaction of ID4 was observed with ID1, ID2 and ID3 that was dependent on intact HLH domain of ID4. Interaction with bHLH protein E47 required almost 3 fold higher concentration of ID4 as compared to ID1. Furthermore, inhibition of E47 DNA binding by ID1 was restored by ID4 in an EMSA binding assay. ID4 and ID1 were also colocalized in prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. The alpha helix forming alanine stretch N-terminal, unique to HLH ID4 domain was required for optimum interaction. Ectopic expression of ID4 in DU145 prostate cancer line promoted E47 dependent expression of CDKNI p21. Thus counteracting the biological activities of ID-1, -2 and -3 by forming inactive heterodimers appears to be a novel mechanism of action of ID4. These results could have far reaching consequences in developing strategies to target ID proteins for cancer therapy and understanding biologically relevant ID-interactions.
Keywords: Cancer; DNA-Protein interaction; ID4; Protein–protein interaction; Tumor suppressor gene.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. and Société Française de Biochimie et Biologie Moléculaire (SFBBM). All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hormonal regulation and differential actions of the helix-loop-helix transcriptional inhibitors of differentiation (Id1, Id2, Id3, and Id4) in Sertoli cells.Endocrinology. 2001 May;142(5):1727-36. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.5.8134. Endocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11316735
-
The expression pattern of Id4, a novel dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein, is distinct from Id1, Id2 and Id3.Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 11;22(5):749-55. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.5.749. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. PMID: 8139914 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of differentiation 1 (Id1) and Id3 proteins play different roles in TGFβ effects on cell proliferation and migration in prostate cancer cells.Prostate. 2013 May;73(6):624-33. doi: 10.1002/pros.22603. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Prostate. 2013. PMID: 23060149 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4): From development to cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1855(1):92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25512197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Id proteins: small molecules, mighty regulators.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;110:189-216. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-405943-6.00005-1. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25248477 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of Lumen Formation in a Three-dimensional Model of Mammary Morphogenesis by Transcriptional Regulator ID4: ROLE OF CaMK2D IN THE EPIGENETIC REGULATION OF ID4 GENE EXPRESSION.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 5;291(32):16766-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.710160. Epub 2016 Jun 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27302061 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of the Intrinsically Disordered Regions for the Functions of the bHLH Transcription Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 24;20(21):5306. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215306. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31653121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and Prognostic Value of Id-4 in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Feb 12;13:1225-1234. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S230678. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32103990 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic values of the inhibitor of DNA‑binding family members in breast cancer.Oncol Rep. 2018 Oct;40(4):1897-1906. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6589. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30066902 Free PMC article.
-
HES1 protein oscillations are necessary for neural stem cells to exit from quiescence.iScience. 2021 Oct 2;24(10):103198. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103198. eCollection 2021 Oct 22. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34703994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murre C, Bain G, van Dijk MA, Engel I, Furnari BA, Massari ME, Matthews JR, Quong MW, Rivera RR, Stuiver MH. Structure and function of helix-loop-helix proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1218(2):129–135. - PubMed
-
- Murre C, McCaw PS, Vaessin H, Caudy M, Jan LY, Jan YN, Cabrera CV, Buskin JN, Hauschka SD, Lassar AB, Weintraub H, Baltimore D. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989;58(3):537–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

