Fatty acid binding protein 5 promotes metastatic potential of triple negative breast cancer cells through enhancing epidermal growth factor receptor stability
- PMID: 25779666
- PMCID: PMC4467443
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3442
Fatty acid binding protein 5 promotes metastatic potential of triple negative breast cancer cells through enhancing epidermal growth factor receptor stability
Abstract
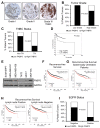
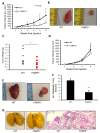
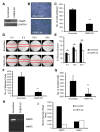
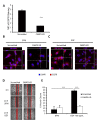
Fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5), an intracellular lipid binding protein, has been shown to play a role in various cancers, including breast cancer. However, FABP5 and its role in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) have not been studied. We show FABP5 protein expression correlates with TNBC, high grade tumors, and worse disease-free survival in a tissue microarray containing 423 breast cancer patient samples. High FABP5 expression significantly correlates with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in these samples. Decreased tumor growth and lung metastasis were observed in FABP5-/- mice othotopically injected with murine breast cancer cells. FABP5 loss in TNBC tumor cells inhibited motility and invasion. Mechanistic studies revealed that FABP5 knockdown in TNBC cells results in decreased EGFR expression and FABP5 is important for EGF-induced metastatic signaling. Loss of FABP5 leads to proteasomal targeting of EGFR. Our studies show that FABP5 has a role in both host and tumor cell during breast cancer progression. These findings suggest that FABP5 mediates its enhanced effect on TNBC metastasis, in part, through EGFR, by inhibiting EGFR proteasomal degradation. These studies show, for the first time, a correlation between FABP5 and EGFR in enhancing TNBC metastasis through a novel mechanism.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor; fatty acid binding protein 5; metastasis; protein degradation; triple negative breast cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic ablation of the fatty acid-binding protein FABP5 suppresses HER2-induced mammary tumorigenesis.Cancer Res. 2013 Aug 1;73(15):4770-80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0384. Epub 2013 May 30. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23722546 Free PMC article.
-
Nitro-fatty acid inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer cell viability, migration, invasion, and tumor growth.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 26;293(4):1120-1137. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.814368. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29158255 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 signaling through sphingosine kinase-1 sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer cells to EGF receptor blockade.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Feb;13(2):316-28. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0367. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24337110
-
The emerging role of fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) in cancers.Drug Discov Today. 2023 Jul;28(7):103628. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103628. Epub 2023 May 23. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 37230284 Review.
-
Recent treatment progress of triple negative breast cancer.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020 Mar;151:40-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31761352 Review.
Cited by
-
An Amplified Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Gene Cluster in Prostate Cancer: Emerging Roles in Lipid Metabolism and Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 18;12(12):3823. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123823. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33352874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty-Acid-Binding Proteins: From Lipid Transporters to Disease Biomarkers.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 6;13(12):1753. doi: 10.3390/biom13121753. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose-Derived Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins Plasma Concentrations Are Increased in Breast Cancer Patients.Oncologist. 2017 Nov;22(11):1309-1315. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0483. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28701570 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Binding Protein 5 (FABP5) Promotes Aggressiveness of Gastric Cancer Through Modulation of Tumor Immunity.J Gastric Cancer. 2023 Apr;23(2):340-354. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2023.23.e19. J Gastric Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37129157 Free PMC article.
-
A novel fatty acid-binding protein 5-estrogen-related receptor α signaling pathway promotes cell growth and energy metabolism in prostate cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2018 Aug 3;9(60):31753-31770. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25878. eCollection 2018 Aug 3. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30167092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madsen P, Rasmussen HH, Leffers H, Honore B, Celis JE. Molecular Cloning and Expression of a Novel Keratinocyte Protein (Psoriasis-associated fatty acid-binding protein [PA-FABP]) that Is Highly Up-Regulated in Psoriatic Skin and that Shares Similarity to Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1992;99:299–305. - PubMed
-
- Miyake T, Ogawa E, Mikoshiba A, Kobayashi A, Hosoe H, Kashiwabara S, Uhara H, Owada Y, Okuyama R. Epidermal-type FABP is a predictive marker of clinical response to systemic treatment and ultraviolet therapy in psoriatic skin lesions. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012;68:199–202. - PubMed
-
- Babaev VR, Runner RP, Fan D, Ding L, Zhang Y, Tao H, Erbay E, Görgün CZ, Fazio S, Hotamisligil GS, Linton MF. Macrophage Mal1 Deficiency Suppresses Atherosclerosis in Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Null Mice by Activating Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor- -Regulated Genes. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2011;31:1283–90. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

