Universal and individual characteristics of postural sway during quiet standing in healthy young adults
- PMID: 25780094
- PMCID: PMC4393163
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12329
Universal and individual characteristics of postural sway during quiet standing in healthy young adults
Abstract
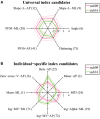
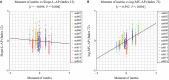
The time course of the center of pressure (CoP) during human quiet standing, corresponding to body sway, is a stochastic process, influenced by a variety of features of the underlying neuro-musculo-skeletal system, such as postural stability and flexibility. Due to complexity of the process, sway patterns have been characterized in an empirical way by a number of indices, such as sway size and mean sway velocity. Here, we describe a statistical approach with the aim of estimating "universal" indices, namely parameters that are independent of individual body characteristics and thus are not "hidden" by the presence of individual, daily, and circadian variations of sway; in this manner it is possible to characterize the common aspects of sway dynamics across healthy young adults, in the assumption that they might reflect underlying neural control during quiet standing. Such universal indices are identified by analyzing intra and inter-subject variability of various indices, after sorting out individual-specific indices that contribute to individual discriminations. It is shown that the universal indices characterize mainly slow components of sway, such as scaling exponents of power-law behavior at a low-frequency regime. On the other hand, most of the individual-specific indices contributing to the individual discriminations exhibit significant correlation with body parameters, and they can be associated with fast oscillatory components of sway. These results are consistent with a mechanistic hypothesis claiming that the slow and the fast components of sway are associated, respectively, with neural control and biomechanics, supporting our assumption that the universal characteristics of postural sway might represent neural control strategies during quiet standing.
Keywords: Intermittent control; postural control; postural sway; slow component.
© 2015 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures
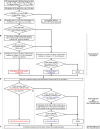

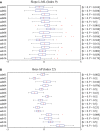
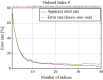

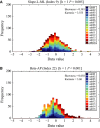

References
-
- Agostini V, Chiaramello E, Canavese L, Bredariol C. Knaflitz M. Postural sway in volleyball players. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2013;32:445–456. - PubMed
-
- Baratto L, Morasso P, Re C. Spada G. A new look at posturographic analysis in the clinical context: sway-density vs. other parameterization techniques. Mot. Control. 2002;6:246–270. - PubMed
-
- Bosek M, Grzegorzewski B, Kowalczyk A. Lubiński I. Degradation of postural control system as a consequence of Parkinson's disease and ageing. Neurosci. Lett. 2005;376:215–220. - PubMed
-
- Bottaro A, Casadio M, Morasso PG. Sanguineti V. Body sway during quiet standing: is it the residual chattering of an intermittent stabilization process? Hum. Mov. Sci. 2005;24:588–615. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

