Cross-modality PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT imaging for pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 25780297
- PMCID: PMC4356919
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2988
Cross-modality PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT imaging for pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Aim: To explore the diagnostic value of the cross-modality fusion images provided by positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) and contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) for pancreatic cancer (PC).
Methods: Data from 70 patients with pancreatic lesions who underwent CECT and PET/CT examinations at our hospital from August 2010 to October 2012 were analyzed. PET/CECT for the cross-modality image fusion was obtained using TureD software. The diagnostic efficiencies of PET/CT, CECT and PET/CECT were calculated and compared with each other using a χ(2) test. P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results: Of the total 70 patients, 50 had PC and 20 had benign lesions. The differences in the sensitivity, negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy between CECT and PET/CECT in detecting PC were statistically significant (P < 0.05 for each). In 15 of the 31 patients with PC who underwent a surgical operation, peripancreatic vessel invasion was verified. The differences in the sensitivity, positive predictive value, NPV, and accuracy of CECT vs PET/CT and PET/CECT vs PET/CT in diagnosing peripancreatic vessel invasion were statistically significant (P < 0.05 for each). In 19 of the 31 patients with PC who underwent a surgical operation, regional lymph node metastasis was verified by postsurgical histology. There was no statistically significant difference among the three methods in detecting regional lymph node metastasis (P > 0.05 for each). In 17 of the 50 patients with PC confirmed by histology or clinical follow-up, distant metastasis was confirmed. The differences in the sensitivity and NPV between CECT and PET/CECT in detecting distant metastasis were statistically significant (P < 0.05 for each).
Conclusion: Cross-modality image fusion of PET/CT and CECT is a convenient and effective method that can be used to diagnose and stage PC, compensating for the defects of PET/CT and CECT when they are conducted individually.
Keywords: Contrast enhancement; Diagnostic imaging; Pancreatic neoplasms; Positron-emission tomography; Staging; Tomography, X-ray computed.
Figures
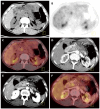
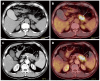
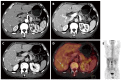
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2004;363:1049–1057. - PubMed
-
- Kim MJ, Lee KH, Lee KT, Lee JK, Ku BH, Oh CR, Heo JS, Choi SH, Choi DW. The value of positron emission tomography/computed tomography for evaluating metastatic disease in patients with pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 2012;41:897–903. - PubMed
-
- Saito M, Ishihara T, Tada M, Tsuyuguchi T, Mikata R, Sakai Y, Tawada K, Sugiyama H, Kurosawa J, Otsuka M, et al. Use of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography with dual-phase imaging to identify intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Lee JW, Kang CM, Choi HJ, Lee WJ, Song SY, Lee JH, Lee JD. Prognostic Value of Metabolic Tumor Volume and Total Lesion Glycolysis on Preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:898–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

