Doxapram hastens the recovery following total intravenous anesthesia with dexmedetomidine, propofol and remifentanil
- PMID: 25780462
- PMCID: PMC4353763
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2015.2249
Doxapram hastens the recovery following total intravenous anesthesia with dexmedetomidine, propofol and remifentanil
Abstract
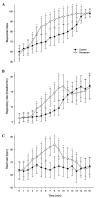
Dexmedetomidine is a suitable sedative for awake fiberoptic intubation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). However, previous studies have shown that dexmedetomidine delays recovery from propofol-remifentanil anesthesia. This study aimed to determine whether doxapram may hasten the recovery following dexmedotomidine-propofol-remifentanil anesthesia. Sixty patients scheduled for uvulopalatopharyngoplasty with total intravenous anesthesia were randomized to two groups according to the medicine given at the end of surgery. These were the doxapram (1 mg/kg) and control (normal saline) groups (n=30 per group). The primary outcome was the time to eye opening on verbal command. The time to return to spontaneous breathing, to hand squeezing in response to verbal command, to extubation of the trachea, and the heart rate (HR), bispectral index (BIS) values, respiratory rate (RR) and pulse oximetry values were also recorded and compared. The time to return to spontaneous breathing (5.2±2.9 vs. 11.7±3.4 min, P<0.001), eye opening (9.3±4.7 vs. 15.9±6.3 min, P<0.001), hand squeeze to command (11.8±6.5 vs. 17.6±7.7 min, P=0.0026) and extubation (14.2±7.8 vs. 19.2±9.6 min, P=0.0308) were significantly shorter in the doxapram group compared with the control group. BIS scores (at 3-14 min), RR (at 4-10 min) and HR (at 2-13 min) were significantly higher in the doxapram group compared with those in the control group (P<0.05). Doxapram hastens the recovery from dexmedetomidine-propofol-remifentanil anesthesia in patients undergoing uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, and may benefit patients with OSA.
Keywords: dexmedetomidine; doxapram; obstructive sleep apnea; propofol; remifentanil.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the recovery and respiratory effects of aminophylline and doxapram following total intravenous anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil.J Clin Anesth. 2013 May;25(3):173-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2012.07.005. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Clin Anesth. 2013. PMID: 23583458 Clinical Trial.
-
Doxapram shortens recovery following sevoflurane anesthesia.Can J Anaesth. 2006 May;53(5):456-60. doi: 10.1007/BF03022617. Can J Anaesth. 2006. PMID: 16636029 Clinical Trial.
-
Remifentanil-propofol vs dexmedetomidine-propofol--anesthesia for supratentorial craniotomy.Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2009 Feb;20(1):63-70. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2009. PMID: 19266828 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of low-dose dexmedetomidine on hemodynamics and anesthetic requirement during bis-spectral index-guided total intravenous anesthesia.J Clin Monit Comput. 2016 Aug;30(4):429-35. doi: 10.1007/s10877-015-9735-2. Epub 2015 Jul 11. J Clin Monit Comput. 2016. PMID: 26162785 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of hemodynamics, recovery profile, and early postoperative pain control and costs of remifentanil versus alfentanil-based total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA).J Clin Anesth. 2002 May;14(3):161-8. doi: 10.1016/s0952-8180(01)00368-3. J Clin Anesth. 2002. PMID: 12031745 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Cricothyroid Membrane Puncture Anesthesia and Topical Anesthesia for Awake Fiberoptic Intubation: A Double-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 16;8:743009. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.743009. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34869434 Free PMC article.
-
Doxapram alleviates low SpO2 induced by the combination of propofol and fentanyl during painless gastrointestinal endoscopy.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 Nov 22;19(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0860-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 31757206 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reversal agents in anaesthesia and critical care.Indian J Anaesth. 2015 Oct;59(10):664-9. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.167484. Indian J Anaesth. 2015. PMID: 26644615 Free PMC article.
-
Time to Wake Up! The Ongoing Search for General Anesthetic Reversal Agents.Anesthesiology. 2024 Mar 1;140(3):610-627. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004846. Anesthesiology. 2024. PMID: 38349760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gross JB, Bachenberg KL, Benumof JL, et al. American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Management. Practice Guidelines for the Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Practice guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Management of patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:1081–1093. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200605000-00026. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous