AUY922 effectively overcomes MET- and AXL-mediated resistance to EGFR-TKI in lung cancer cells
- PMID: 25780909
- PMCID: PMC4363657
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119832
AUY922 effectively overcomes MET- and AXL-mediated resistance to EGFR-TKI in lung cancer cells
Abstract
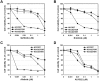
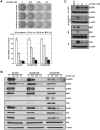
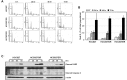
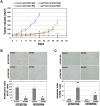
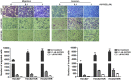
The activation of bypass signals, such as MET and AXL, has been identified as a possible mechanism of EGFR-TKI resistance. Because various oncoproteins depend on HSP90 for maturation and stability, we investigated the effects of AUY922, a newly developed non-geldanamycin class HSP90 inhibitor, in lung cancer cells with MET- and AXL-mediated resistance. We established resistant cell lines with HCC827 cells harboring an exon 19-deletion mutation in of the EGFR gene via long-term exposure to increasing concentrations of gefitinib and erlotinib (HCC827/GR and HCC827/ER, respectively). HCC827/GR resistance was mediated by MET activation, whereas AXL activation caused resistance in HCC827/ER cells. AUY922 treatment effectively suppressed proliferation and induced cell death in both resistant cell lines. Accordingly, the downregulation of EGFR, MET, and AXL led to decreased Akt activation. The inhibitory effects of AUY922 on each receptor were confirmed in gene-transfected LK2 cells. AUY922 also effectively controlled tumor growth in xenograft mouse models containing HCC827/GR and HCC827/ER cells. In addition, AUY922 reduced invasion and migration by both types of resistant cells. Our study findings thus show that AUY922 is a promising therapeutic option for MET- and AXL-mediated resistance to EGFR-TKI in lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MET and AXL inhibitor NPS-1034 exerts efficacy against lung cancer cells resistant to EGFR kinase inhibitors because of MET or AXL activation.Cancer Res. 2014 Jan 1;74(1):253-62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1103. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24165158
-
AXL/MET dual inhibitor, CB469, has activity in non-small cell lung cancer with acquired resistance to EGFR TKI with AXL or MET activation.Lung Cancer. 2020 Aug;146:70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.05.031. Epub 2020 May 29. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32521387
-
Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 enhances the radiation sensitivity of lung cancer cell lines with acquired resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncol Rep. 2015 Mar;33(3):1499-504. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3735. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25607753
-
Combined effect of cabozantinib and gefitinib in crizotinib-resistant lung tumors harboring ROS1 fusions.Cancer Sci. 2018 Oct;109(10):3149-3158. doi: 10.1111/cas.13752. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 30053332 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to overcome acquired resistance to EGFR TKI in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 Oct;21(10):1287-1301. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02075-1. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30864018 Review.
Cited by
-
Anexelekto (AXL) Increases Resistance to EGFR-TKI and Activation of AKT and ERK1/2 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Oncol Res. 2016;24(5):295-303. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14648701447814. Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 27712586 Free PMC article.
-
89Zr-Onartuzumab PET imaging of c-MET receptor dynamics.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017 Aug;44(8):1328-1336. doi: 10.1007/s00259-017-3672-x. Epub 2017 Mar 19. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28315949 Free PMC article.
-
Behind the Wheel of Epithelial Plasticity in KRAS-Driven Cancers.Front Oncol. 2019 Oct 11;9:1049. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01049. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31681587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple receptor tyrosine kinase activation related to ALK inhibitor resistance in lung cancer cells with ALK rearrangement.Oncotarget. 2017 May 8;8(35):58771-58780. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17680. eCollection 2017 Aug 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28938595 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Heat Shock Protein 90 Inhibition on the Proteomic Profile of Lung Adenocarcinoma as Measured by Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis Coupled with Mass Spectrometry.Cells. 2019 Jul 31;8(8):806. doi: 10.3390/cells8080806. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31370342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond LA, Rowinsky EK, Huberman M, Karp D, et al. Determinants of tumor response and survival with erlotinib in patients with non—small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22: 3238–3247. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352: 786–792. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007;316: 1039–1043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

