Pelvic belt effects on pelvic morphometry, muscle activity and body balance in patients with sacroiliac joint dysfunction
- PMID: 25781325
- PMCID: PMC4364533
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116739
Pelvic belt effects on pelvic morphometry, muscle activity and body balance in patients with sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Abstract
Introduction: The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is frequently involved in low back and pelvic girdle pain. However, morphometrical and functional characteristics related to SIJ pain are poorly defined. Pelvic belts represent one treatment option, but evidence still lacks as to their pain-reducing effects and the mechanisms involved. Addressing these two issues, this case-controlled study compares morphometric, functional and clinical data in SIJ patients and healthy controls and evaluates the effects of short-term pelvic belt application.
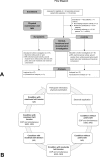
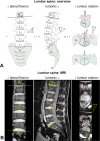
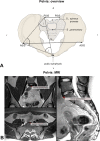
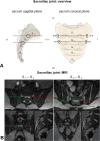
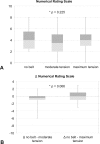
Methods: Morphometric and functional data pertaining to pelvic belt effects were compared in 17 SIJ patients and 17 controls. Lumbar spine and pelvis morphometries were obtained from 3T magnetic resonance imaging. Functional electromyography data of pelvis and leg muscles and center of pressure excursions were measured in one-leg stance. The numerical rating scale was used to evaluate immediate pain-reducing effects.
Results: Pelvic morphometry was largely unaltered in SIJ patients and also by pelvic belt application. The angle of lumbar lateral flexion was significantly larger in SIJ patients without belt application. Muscle activity and center of pressure were unaffected by SIJ pain or by belt application in one-leg stance. Nine of 17 patients reported decreased pain intensities under moderate belt application, four reported no change and four reported increased pain intensity. For the entire population investigated here, this qualitative description was not confirmed on a statistical significant level.
Discussion: Minute changes were observed in the alignment of the lumbar spine in the frontal plane in SIJ patients. The potential pain-decreasing effects of pelvic belts could not be attributed to altered muscle activity, pelvic morphometry or body balance in a static short-term application. Long-term belt effects will therefore be of prospective interest.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Cohen SP. Sacroiliac joint pain: a comprehensive review of anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Anesth Analg. 2005;101(5): 1440–1453. - PubMed
-
- Forst SL, Wheeler MT, Fortin JD, Vilensky JA. The sacroiliac joint: anatomy, physiology and clinical significance. Pain Physician. 2006;9(1): 61–67. - PubMed
-
- Fortin JD, Kissling RO, O'Connor BL, Vilensky JA. Sacroiliac joint innervation and pain. Am J Orthop. 1999;28 (12): 687–690. - PubMed
-
- Laplante BL, Ketchum JM, Saullo TR, DePalma MJ. Multivariable analysis of the relationship between pain referral patterns and the source of chronic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2012;15(2): 171–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

