Transcriptome analysis of maize leaf systemic symptom infected by Bipolaris zeicola
- PMID: 25781606
- PMCID: PMC4363367
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119858
Transcriptome analysis of maize leaf systemic symptom infected by Bipolaris zeicola
Abstract
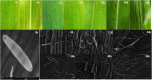
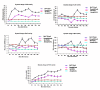
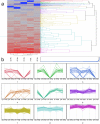
Bipolaris zeicola is a fungal pathogen that causes Northern corn leaf spot (NCLS), which is a serious foliar disease in maize and one of the most significant pathogens affecting global food security. Here, we report a genome-wide transcriptional profile analysis using next-generation sequencing (NGS) of maize leaf development after inoculation with B. zeicola. We performed High-Throughput Digital Gene Expression analysis to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in resistant inbred Mo17 lines after infection with B. zeicola at four successive disease development stages--CP (contact period), PP (penetration period), IP (incubation period), and DP (disease period); the expression of the genes was compared with those in a CK (mock-treatment) control. In addition, a sensitive maize line (Zheng58) was used for the comparisons with the Mo17. Among all tested genes, 466 differentially expressed genes were identified in all libraries, and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis of these genes suggested that they are involved in many biological processes related to systemic symptom development, such as plant hormone signal transduction, starch and sucrose metabolism, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and photosynthesis. Our systematic analysis provides comprehensive transcriptomic information regarding systemic symptom development in fungal-infected plants. This information will help in furthering our understanding of the detailed mechanisms of plant responses to fungal infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Expression profile analysis of maize in response to Setosphaeria turcica.Gene. 2018 Jun 15;659:100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.03.030. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29548860
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis highlights resistance regulatory networks of maize in response to Exserohilum turcicum infection at the early stage.Physiol Plant. 2024 Nov-Dec;176(6):e14615. doi: 10.1111/ppl.14615. Physiol Plant. 2024. PMID: 39508116
-
Transcriptome profiling of two maize inbreds with distinct responses to Gibberella ear rot disease to identify candidate resistance genes.BMC Genomics. 2018 Feb 9;19(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4513-4. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29426290 Free PMC article.
-
Barley leaf transcriptome and metabolite analysis reveals new aspects of compatibility and Piriformospora indica-mediated systemic induced resistance to powdery mildew.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011 Dec;24(12):1427-39. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-06-11-0177. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011. PMID: 21830949
-
Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Resistant and Susceptible Sugarcane Cultivars in Response to Infection by Xanthomonas albilineans.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 5;20(24):6138. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246138. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31817492 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The complete mitochondrial genomes of five critical phytopathogenic Bipolaris species: features, evolution, and phylogeny.IMA Fungus. 2024 Jun 11;15(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s43008-024-00149-6. IMA Fungus. 2024. PMID: 38863028 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in maize transcriptome in response to maize Iranian mosaic virus infection.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 10;13(4):e0194592. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194592. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29634778 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation on comparative transcriptome profiling of resistant and susceptible non-CMS maize genotypes during Bipolaris maydis race O infection.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 20;10(5):e26538. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26538. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38434297 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive transcriptome analyses of Northern Wild Rice (Zizania palustris L.) and Bipolaris oryzae show convoluted communications during the early stages of fungal brown spot development.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Apr 26;15:1350281. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1350281. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38736448 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Fungal Pathogen Bipolaris maydis to Understand Pathogenicity Behavior on Resistant and Susceptible Non-CMS Maize Genotypes.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 29;13:837056. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.837056. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35572625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schenck N, Stelter T. Southern corn leaf blight development relative to temperature, moisture and fungicide application. Phytopathology. 1974;64(5):619–624.
-
- Sumner D, Littrell R. Influence of tillage, planting date, inoculum survival, and mixed populations on epidemiology of southern corn leaf blight.Phytopathology. 1974;64(2):168–173.
-
- Welz H, Leonard K. Phenotypic variation and parasitic fitness of races of Cochliobolus carbonum on corn in North Carolina. Phytopathology. 1993;83(6):593–601.
-
- Jones MJ, Dunkle LD. Analysis of Cochliobolus carbonum races by PCR amplification with arbitrary and gene-specific primers. Phytopathology.1993;83:366–366.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

