Olodaterol attenuates citric acid-induced cough in naïve and ovalbumin-sensitized and challenged guinea pigs
- PMID: 25781609
- PMCID: PMC4364307
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119953
Olodaterol attenuates citric acid-induced cough in naïve and ovalbumin-sensitized and challenged guinea pigs
Abstract
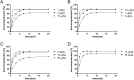
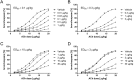
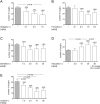
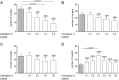
Excessive coughing is a common feature of airway diseases. Different G-protein coupled receptors, including β2-adrenergic receptors (β2-AR), have been implicated in the molecular mechanisms underlying the cough reflex. However, the potential antitussive property of β2-AR agonists in patients with respiratory disease is a matter of ongoing debate. The aim of our study was to test the efficacy of the long-acting β2-AR agonist olodaterol with regard to its antitussive property in a pre-clinical model of citric acid-induced cough in guinea pigs and to compare the results to different clinically relevant β2-AR agonists. In our study β2-AR agonists were intratracheally administered, as dry powder, into the lungs of naïve or ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs 15 minutes prior to induction of cough by exposure to citric acid. Cough events were counted over 15 minutes during the citric acid exposure. Olodaterol dose-dependently inhibited the number of cough events in naïve and even more potently and with a greater maximal efficacy in ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs (p < 0.01). Formoterol and salmeterol showed a trend towards reducing cough. On the contrary, indacaterol demonstrated pro-tussive properties as it significantly increased the number of coughs, both in naïve and ovalbumin-sensitized animals (p < 0.001). In conclusion, olodaterol, at doses eliciting bronchodilation, showed antitussive properties in a model of citric acid-induced cough in naïve and ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs. This is in agreement with pre-clinical and clinical studies showing antitussive efficacy of β2-AR agonists. Indacaterol increased the number of coughs in this model, which concurs with clinical data where a transient cough has been observed after indacaterol inhalation. While the antitussive properties of β2-AR agonists can be explained by their ability to lead to the cAMP-induced hyperpolarization of the neuron membrane thereby inhibiting sensory nerve activation and the cough reflex, the mechanism underlying the pro-tussive property of indacaterol is not known.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of within-group designs to test anti-tussive drugs in conscious guinea-pigs.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2010 Mar-Apr;61(2):157-62. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2010.02.015. Epub 2010 Mar 1. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2010. PMID: 20193769
-
Antitussive effect of moguisteine on allergic coughs in the guinea pig.Eur J Pharmacol. 1998 Apr 24;347(2-3):253-5. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00176-9. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9653890
-
The influence of the PDE inhibitors on cough reflex in guinea pigs.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2011;112(3):131-5. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2011. PMID: 21452764
-
▼Olodaterol--another LABA for COPD.Drug Ther Bull. 2015 Apr;53(4):42-5. doi: 10.1136/dtb.2015.4.0319. Drug Ther Bull. 2015. PMID: 25858815 Review.
-
Antitussive effect of nociceptin/orphanin FQ in experimental cough models.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2002;15(3):213-6. doi: 10.1006/pupt.2002.0357. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12099766 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of cough hypersensitivity with tracheal TRPV1 activation and neurogenic inflammation in a novel guinea pig model of citric acid-induced chronic cough.J Int Med Res. 2018 Jul;46(7):2913-2924. doi: 10.1177/0300060518778951. Epub 2018 Jun 7. J Int Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29877121 Free PMC article.
-
Olodaterol shows anti-fibrotic efficacy in in vitro and in vivo models of pulmonary fibrosis.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;174(21):3848-3864. doi: 10.1111/bph.13982. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28810065 Free PMC article.
-
A Cold Environment Aggravates Cough Hyperreactivity in Guinea Pigs With Cough by Activating the TRPA1 Signaling Pathway in Skin.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 27;11:833. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00833. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32982765 Free PMC article.
-
Ozone-Induced Hypertussive Responses in Rabbits and Guinea Pigs.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Apr;357(1):73-83. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.230227. Epub 2016 Feb 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 26837703 Free PMC article.
-
Cough as an adverse effect on inhalation pharmaceutical products.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;177(18):4096-4112. doi: 10.1111/bph.15197. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32668011 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morice AH, Fontana GA, Sovijarvi AR, Pistolesi M, Chung KF, Widdicombe J, et al. The diagnosis and management of chronic cough. Eur Respir J. 2004;24: 481–492. - PubMed
-
- Prudon B, Birring SS, Vara DD, Hall AP, Thompson JP, Pavord ID. Cough and glottic-stop reflex sensitivity in health and disease. Chest. 2005;127: 550–557. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

