Sensitization of neonatal rat lumbar motoneuron by the inflammatory pain mediator bradykinin
- PMID: 25781633
- PMCID: PMC4410746
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.06195
Sensitization of neonatal rat lumbar motoneuron by the inflammatory pain mediator bradykinin
Abstract
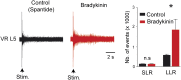
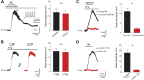
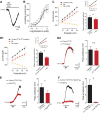
Bradykinin (Bk) is a potent inflammatory mediator that causes hyperalgesia. The action of Bk on the sensory system is well documented but its effects on motoneurons, the final pathway of the motor system, are unknown. By a combination of patch-clamp recordings and two-photon calcium imaging, we found that Bk strongly sensitizes spinal motoneurons. Sensitization was characterized by an increased ability to generate self-sustained spiking in response to excitatory inputs. Our pharmacological study described a dual ionic mechanism to sensitize motoneurons, including inhibition of a barium-sensitive resting K(+) conductance and activation of a nonselective cationic conductance primarily mediated by Na(+). Examination of the upstream signaling pathways provided evidence for postsynaptic activation of B2 receptors, G protein activation of phospholipase C, InsP3 synthesis, and calmodulin activation. This study questions the influence of motoneurons in the assessment of hyperalgesia since the withdrawal motor reflex is commonly used as a surrogate pain model.
Keywords: hyperalgesia; motoneuron; neuroscience; pain; rat; spinal cord.
Conflict of interest statement
BR: Founder of Femtonics Ltd and a member of its scientific advisory board.
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Substance P release evoked by capsaicin or potassium from rat cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons is conversely modulated with bradykinin.J Neurochem. 2006 Jun;97(5):1412-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03830.x. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16696851
-
Sensitization of vanilloid receptor 1 induced by bradykinin via the activation of second messenger signaling cascades in rat primary afferent neurons.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 13;498(1-3):37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.076. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15363973
-
Sympathoexcitation by bradykinin involves Ca2+-independent protein kinase C.J Neurosci. 2002 Jul 15;22(14):5823-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-14-05823.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12122044 Free PMC article.
-
Depolarizing Effectors of Bradykinin Signaling in Nociceptor Excitation in Pain Perception.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018 May 1;26(3):255-267. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2017.127. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018. PMID: 29378387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 6 Regulation in Inflammation and Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 14;23(24):15880. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415880. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555521 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trpm5 channels encode bistability of spinal motoneurons and ensure motor control of hindlimbs in mice.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 24;12(1):6815. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27113-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34819493 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of bradykinin and bradykinin B1 receptor in patients with endometriosis.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Nov;22(5):1240. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10675. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34539836 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitization and Interoception as Key Neurological Concepts in Osteopathy and Other Manual Medicines.Front Neurosci. 2016 Mar 10;10:100. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00100. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27013961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The M-current works in tandem with the persistent sodium current to set the speed of locomotion.PLoS Biol. 2020 Nov 13;18(11):e3000738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000738. eCollection 2020 Nov. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 33186352 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interplay in chronic pain: The calcium connection.Mol Pain. 2020 Jan-Dec;16:1744806920946889. doi: 10.1177/1744806920946889. Mol Pain. 2020. PMID: 32787562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bleasdale JE, Thakur NR, Gremban RS, Bundy GL, Fitzpatrick FA, Smith RJ, Bunting S. Selective inhibition of receptor-coupled phospholipase C-dependent processes in human platelets and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1990;255:756–768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

