Increased ventral-striatal activity during monetary decision making is a marker of problem poker gambling severity
- PMID: 25781641
- PMCID: PMC4573763
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.12239
Increased ventral-striatal activity during monetary decision making is a marker of problem poker gambling severity
Abstract
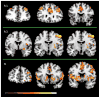
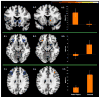
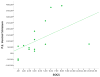
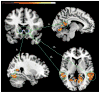
The aim of this study was to examine the impact of different neural systems on monetary decision making in frequent poker gamblers, who vary in their degree of problem gambling. Fifteen frequent poker players, ranging from non-problem to high-problem gambling, and 15 non-gambler controls were scanned using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) while performing the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT). During IGT deck selection, between-group fMRI analyses showed that frequent poker gamblers exhibited higher ventral-striatal but lower dorsolateral prefrontal and orbitofrontal activations as compared with controls. Moreover, using functional connectivity analyses, we observed higher ventral-striatal connectivity in poker players, and in regions involved in attentional/motor control (posterior cingulate), visual (occipital gyrus) and auditory (temporal gyrus) processing. In poker gamblers, scores of problem gambling severity were positively associated with ventral-striatal activations and with the connectivity between the ventral-striatum seed and the occipital fusiform gyrus and the middle temporal gyrus. Present results are consistent with findings from recent brain imaging studies showing that gambling disorder is associated with heightened motivational-reward processes during monetary decision making, which may hamper one's ability to moderate his level of monetary risk taking.
Keywords: Decision making; fMRI; problem gambling severity; ventral striatum.
© 2015 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neural substrates of cue reactivity and craving in gambling disorder.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 3;7(1):e992. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.256. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28045460 Free PMC article.
-
Increased corticolimbic connectivity in cocaine dependence versus pathological gambling is associated with drug severity and emotion-related impulsivity.Addict Biol. 2016 May;21(3):709-18. doi: 10.1111/adb.12242. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Addict Biol. 2016. PMID: 25818325
-
Neural correlates of the impact of prior outcomes on subsequent monetary decision-making in frequent poker players.Biol Psychol. 2017 Mar;124:30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2017.01.009. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Biol Psychol. 2017. PMID: 28126429
-
Neuroimaging of reward mechanisms in Gambling disorder: an integrative review.Mol Psychiatry. 2019 May;24(5):674-693. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0230-2. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Mol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30214041 Review.
-
[Decision-making and schizophrenia].Encephale. 2011 Dec;37 Suppl 2:S110-6. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7006(11)70036-7. Encephale. 2011. PMID: 22212839 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Spatio-temporal EEG dynamics during decision-making in online poker players with problem gambling.J Behav Addict. 2024 Sep 4;13(3):768-778. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00048. Print 2024 Oct 4. J Behav Addict. 2024. PMID: 39235871 Free PMC article.
-
Altered orbitofrontal sulcogyral patterns in gambling disorder: a multicenter study.Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 5;9(1):186. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0520-8. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31383841 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and Neural Arguments of Motivational Influence on Decision Making During Uncertainty.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jun 5;14:583. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00583. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32581698 Free PMC article.
-
Reinforcement Sensitivity Theory and Problem Gambling in a General Population Sample.J Gambl Stud. 2019 Dec;35(4):1163-1175. doi: 10.1007/s10899-019-09850-3. J Gambl Stud. 2019. PMID: 31055690
-
The orbitofrontal cortex represents advantageous choice in the Iowa gambling task.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Aug 15;43(12):3840-3856. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25887. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 35476367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
-
- Bechara A. Decision Making, Impulse Control and Loss of Willpower to Resist Drugs: A Neurocognitive Perspective. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1458–1463. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A, Damasio AR. The somatic marker hypothesis: A neural theory of economic decision. Game Econ Behav. 2005;52:336–372.
-
- Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio AR. Emotion, decision-making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2000;10:295–307. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A, Damasio AR, Damasio H, Anderson SW. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition. 1994;50:7–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

