A novel mouse model for stable engraftment of a human immune system and human hepatocytes
- PMID: 25782010
- PMCID: PMC4364106
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119820
A novel mouse model for stable engraftment of a human immune system and human hepatocytes
Abstract
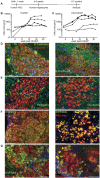
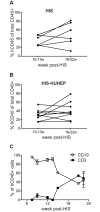
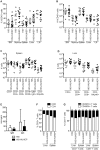
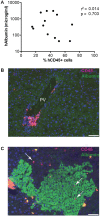
Hepatic infections by hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV) and Plasmodium parasites leading to acute or chronic diseases constitute a global health challenge. The species tropism of these hepatotropic pathogens is restricted to chimpanzees and humans, thus model systems to study their pathological mechanisms are severely limited. Although these pathogens infect hepatocytes, disease pathology is intimately related to the degree and quality of the immune response. As a first step to decipher the immune response to infected hepatocytes, we developed an animal model harboring both a human immune system (HIS) and human hepatocytes (HUHEP) in BALB/c Rag2-/- IL-2Rγc-/- NOD.sirpa uPAtg/tg mice. The extent and kinetics of human hepatocyte engraftment were similar between HUHEP and HIS-HUHEP mice. Transplanted human hepatocytes were polarized and mature in vivo, resulting in 20-50% liver chimerism in these models. Human myeloid and lymphoid cell lineages developed at similar frequencies in HIS and HIS-HUHEP mice, and splenic and hepatic compartments were humanized with mature B cells, NK cells and naïve T cells, as well as monocytes and dendritic cells. Taken together, these results demonstrate that HIS-HUHEP mice can be stably (> 5 months) and robustly engrafted with a humanized immune system and chimeric human liver. This novel HIS-HUHEP model provides a platform to investigate human immune responses against hepatotropic pathogens and to test novel drug strategies or vaccine candidates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2006;1: 23–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

