Targeting protein neddylation with an NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induced apoptosis or senescence in human lymphoma cells
- PMID: 25782162
- PMCID: PMC4623239
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2014.1003003
Targeting protein neddylation with an NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induced apoptosis or senescence in human lymphoma cells
Abstract
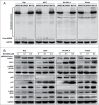
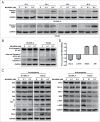
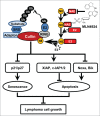
Recent studies indicate that post-translational protein neddylation is required for the maintenance of cell viability in several lymphoma cell lines, while inhibition of the neddylation pathway with an NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibitor MLN4924 induces apoptosis in lymphoma cells. However, the mechanism by which neddylation inhibition induces apoptosis in lymphoma cells has not been fully elucidated. Moreover, it is unknown whether neddylation inhibition triggers non-apoptotic cell-killing responses, such as cell senescence, in lymphoma cells. Here, we report that MLN4924 specifically inhibited protein neddylation, inactivated cullin-RING E3 ligase (CRL), the best-known neddylation substrate, and induced the accumulation of tumor-suppressive CRL substrates in lymphoma cells. Moreover, MLN4924 potently suppressed the growth of lymphoma cells by inducing G2 cell-cycle arrest, followed by apoptosis or senescence in a cell line-dependent manner. MLN4924-induced apoptosis was mediated by intrinsic apoptotic signaling with substantial up-regulation of pro-apoptotic Bik and Noxa as well as down-regulation of anti-apoptotic XIAP, c-IAP1 and c-IAP2, while senescence induction upon neddylation inhibition seemed dependent on the expression of tumor suppressor p21/p27. Together, these findings expand our understanding on how lymphoma cells respond to neddylation inhibition and support the development of neddylation inhibitors (e.g. MLN4924) for the treatment of lymphoma.
Keywords: CRL, cullin-RING E3 ligase; GCB-DLBCL, germinal-center B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; IAP, inhibitor of apoptosis; MLN4924; NAE, NEDD8-activating enzyme; NHL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma; SA-β-gal, senescence-associated β-galactosidase; apoptosis; lymphoma; neddylation; senescence.
Figures


References
-
- Xirodimas DP. Novel substrates and functions for the ubiquitin-like molecule NEDD8. Biochem Soc Trans 2008; 36:802-6; PMID:18793140; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1042/BST0360802 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rabut G, Peter M. Function and regulation of protein neddylation. 'Protein modifications: beyond the usual suspects' review series. EMBO Rep 2008; 9:969-76; PMID:18802447; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/embor.2008.183 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soucy TA, Dick LR, Smith PG, Milhollen MA, Brownell JE. The NEDD8 Conjugation Pathway and Its Relevance in Cancer Biology and Therapy. Genes Cancer 2010; 1:708-16; PMID:21779466; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1177/1947601910382898 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duncan K, Schafer G, Vava A, Parker MI, Zerbini LF. Targeting neddylation in cancer therapy. Future Oncol 2012; 8:1461-70; PMID:23148618; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.2217/fon.12.131 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang M, Medeiros BC, Erba HP, DeAngelo DJ, Giles FJ, Swords RT. Targeting protein neddylation: a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2011; 15:253-64; PMID:21219242; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1517/14728222.2011.550877 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
