The Arabidopsis RNA-binding protein AtRGGA regulates tolerance to salt and drought stress
- PMID: 25783413
- PMCID: PMC4424017
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.255802
The Arabidopsis RNA-binding protein AtRGGA regulates tolerance to salt and drought stress
Abstract
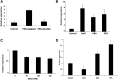
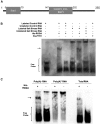
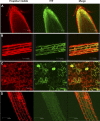
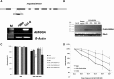
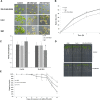
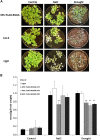
Salt and drought stress severely reduce plant growth and crop productivity worldwide. The identification of genes underlying stress response and tolerance is the subject of intense research in plant biology. Through microarray analyses, we previously identified in potato (Solanum tuberosum) StRGGA, coding for an Arginine Glycine Glycine (RGG) box-containing RNA-binding protein, whose expression was specifically induced in potato cell cultures gradually exposed to osmotic stress. Here, we show that the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) ortholog, AtRGGA, is a functional RNA-binding protein required for a proper response to osmotic stress. AtRGGA gene expression was up-regulated in seedlings after long-term exposure to abscisic acid (ABA) and polyethylene glycol, while treatments with NaCl resulted in AtRGGA down-regulation. AtRGGA promoter analysis showed activity in several tissues, including stomata, the organs controlling transpiration. Fusion of AtRGGA with yellow fluorescent protein indicated that AtRGGA is localized in the cytoplasm and the cytoplasmic perinuclear region. In addition, the rgga knockout mutant was hypersensitive to ABA in root growth and survival tests and to salt stress during germination and at the vegetative stage. AtRGGA-overexpressing plants showed higher tolerance to ABA and salt stress on plates and in soil, accumulating lower levels of proline when exposed to drought stress. Finally, a global analysis of gene expression revealed extensive alterations in the transcriptome under salt stress, including several genes such as ASCORBATE PEROXIDASE2, GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE TAU9, and several SMALL AUXIN UPREGULATED RNA-like genes showing opposite expression behavior in transgenic and knockout plants. Taken together, our results reveal an important role of AtRGGA in the mechanisms of plant response and adaptation to stress.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A stress-responsive caleosin-like protein, AtCLO4, acts as a negative regulator of ABA responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2011 May;52(5):874-84. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr039. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21471120
-
The CONSTANS-like 4 transcription factor, AtCOL4, positively regulates abiotic stress tolerance through an abscisic acid-dependent manner in Arabidopsis.J Integr Plant Biol. 2015 Mar;57(3):313-24. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12246. Epub 2014 Sep 9. J Integr Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25073793
-
A Nucleus-Localized Long Non-Coding RNA Enhances Drought and Salt Stress Tolerance.Plant Physiol. 2017 Nov;175(3):1321-1336. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00574. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28887353 Free PMC article.
-
Interconnection of iron and osmotic stress signalling in plants: is FIT a regulatory hub to cross-connect abscisic acid responses?Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2021 May;23 Suppl 1:31-38. doi: 10.1111/plb.13261. Epub 2021 May 13. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2021. PMID: 33772999 Review.
-
Regulation of mRNA decay in plant responses to salt and osmotic stress.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Apr;74(7):1165-1176. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2376-x. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27677492 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterologous Expression of Arabidopsis AtARA6 in Soybean Enhances Salt Tolerance.Front Genet. 2022 May 12;13:849357. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.849357. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35646070 Free PMC article.
-
Functional, Structural and Biochemical Features of Plant Serinyl-Glutathione Transferases.Front Plant Sci. 2019 May 22;10:608. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00608. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31191562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regulatory Roles of RNA-Binding Proteins in Plant Salt Stress Response.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 7;14(9):1402. doi: 10.3390/plants14091402. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40364430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mRNA-binding protein HLN1 enhances drought stress tolerance by stabilizing the GAD2 mRNA in Arabidopsis.Stress Biol. 2025 Jun 6;5(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s44154-025-00239-4. Stress Biol. 2025. PMID: 40478352 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic signatures of ecological divergence between savanna and forest populations of a Neotropical tree.Ann Bot. 2023 Nov 23;132(3):523-540. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcad120. Ann Bot. 2023. PMID: 37642427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe M, Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Daimon Y, Yamaguchi A, Ikeda Y, Ichinoki H, Notaguchi M, Goto K, Araki T (2005) FD, a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex. Science 309: 1052–1056 - PubMed
-
- Albà MM, Pagès M (1998) Plant proteins containing the RNA-recognition motif. Trends Plant Sci 3: 15–21
-
- Ambrosone A, Costa A, Leone A, Grillo S (2012) Beyond transcription: RNA-binding proteins as emerging regulators of plant response to environmental constraints. Plant Sci 182: 12–18 - PubMed
-
- Ambrosone A, Costa A, Martinelli R, Massarelli I, De Simone V, Grillo S, Leone A (2011) Differential gene regulation in potato cells and plants upon abrupt or gradual exposure to water stress. Acta Physiol Plant 33: 1157–1171
-
- Ambrosone A, Di Giacomo M, Leone A, Grillo MS, Costa A (2013) Identification of early induced genes upon water deficit in potato cell cultures by cDNA-AFLP. J Plant Res 126: 169–178 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

