Aminoglycoside ototoxicity and hair cell ablation in the adult gerbil: A simple model to study hair cell loss and regeneration
- PMID: 25783988
- PMCID: PMC4441107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.03.002
Aminoglycoside ototoxicity and hair cell ablation in the adult gerbil: A simple model to study hair cell loss and regeneration
Abstract
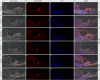
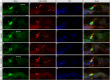
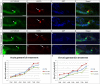
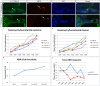
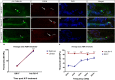
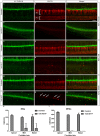
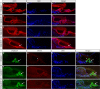
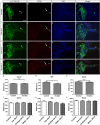
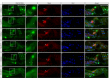
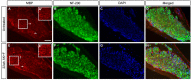
The Mongolian gerbil, Meriones unguiculatus, has been widely employed as a model for studies of the inner ear. In spite of its established use for auditory research, no robust protocols to induce ototoxic hair cell damage have been developed for this species. In this paper, we demonstrate the development of an aminoglycoside-induced model of hair cell loss, using kanamycin potentiated by the loop diuretic furosemide. Interestingly, we show that the gerbil is relatively insensitive to gentamicin compared to kanamycin, and that bumetanide is ineffective in potentiating the ototoxicity of the drug. We also examine the pathology of the spiral ganglion after chronic, long-term hair cell damage. Remarkably, there is little or no neuronal loss following the ototoxic insult, even at 8 months post-damage. This is similar to the situation often seen in the human, where functioning neurons can persist even decades after hair cell loss, contrasting with the rapid, secondary degeneration found in rats, mice and other small mammals. We propose that the combination of these factors makes the gerbil a good model for ototoxic damage by induced hair cell loss.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abrashkin K.A., Izumikawa M., Miyazawa T., Wang C.H., Crumling M.A., Swiderski D.L., Beyer L.A., Gong T.W., Raphael Y. The fate of outer hair cells after acoustic or ototoxic insults. Hear Res. 2006;218:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Alam S.A., Ikeda K., Kawase T., Kikuchi T., Katori Y., Watanabe K., Takasaka T. Acute effects of combined administration of kanamycin and furosemide on the stria vascularis studied by distortion product otoacoustic emission and transmission electron microscopy. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1998;186:79–86. - PubMed
-
- Aran J.M., Darrouzet J. Observation of click-evoked compound VIII nerve responses before, during, and over seven months after kanamycin treatment in the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol. 1975;79:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Astbury P.J., Read N.G. Kanamycin induced ototoxicity in the laboratory rat. A comparative morphological and audiometric study. Arch. Toxicol. 1982;50:267–278. - PubMed
-
- Bae W.Y., Kim L.S., Hur D.Y., Jeong S.W., Kim J.R. Secondary apoptosis of spiral ganglion cells induced by aminoglycoside: Fas-Fas ligand signaling pathway. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:1659–1668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

