HIF-1 at the crossroads of hypoxia, inflammation, and cancer
- PMID: 25784597
- PMCID: PMC4573780
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.29519
HIF-1 at the crossroads of hypoxia, inflammation, and cancer
Abstract
The complex cross-talk of intricate intercellular signaling networks between the tumor and stromal cells promotes cancer progression. Hypoxia is one of the most common conditions encountered within the tumor microenvironment that drives tumorigenesis. Most responses to hypoxia are elicited by a family of transcription factors called hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which induce expression of a diverse set of genes that assist cells to adapt to hypoxic environments. Among the three HIF protein family members, the role of HIF-1 is well established in cancer progression. HIF-1 functions as a signaling hub to coordinate the activities of many transcription factors and signaling molecules that impact tumorigenesis. This mini review discusses the complex role of HIF-1 and its context-dependent partners under various cancer-promoting events including inflammation and generation of cancer stem cells, which are implicated in tumor metastasis and relapse. In addition, the review highlights the importance of therapeutic targeting of HIF-1 for cancer prevention.
Keywords: HIF-1; cancer stem cells; drug resistance; hypoxia; inflammation; microenvironment.
© 2015 UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
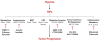
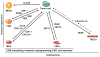
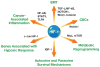
References
-
- Lokmic Z, Musyoka J, Hewitson TD, et al. Hypoxia and hypoxia signaling in tissue repair and fibrosis. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012;296:139–85. - PubMed
-
- Semenza GL. Oxygen sensing, hypoxia-inducible factors and disease pathophysiology. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:47–71. - PubMed
-
- Wenger RH, Stiehl DP, Camenisch G. Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci STKE. 2005;306:re12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

