Impact of different beam directions on intensity-modulated radiation therapy dose delivered to functioning lung tissue identified using single-photon emission computed tomography
- PMID: 25784844
- PMCID: PMC4355654
- DOI: 10.5114/wo.2014.46237
Impact of different beam directions on intensity-modulated radiation therapy dose delivered to functioning lung tissue identified using single-photon emission computed tomography
Abstract
Aim of the study: To use different beam arrangements and numbers to plan intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and investigate their effects on low and high radiation doses delivered to the functional lung, in order to reduce radiation-induced lung damage.
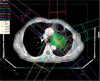
Material and methods: Ten patients with stage I-III non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) underwent IMRT. Beam arrangements were selected on the basis of orientation and dose-volume histograms to create SPECT-guided IMRT plans that spared the functional lung and maintained target coverage. Four different plans, including CT-7, SPECT-7, SPECT-4, SPECT-5 with different beam arrangements, were used. The differences of conformity index (CI), heterogeneity index (HI) between the plans were analyzed, by using a paired t-test.
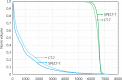
Results: The seven-beam SPECT (SPECT-7) plan reduced the volume of the functional lung irradiated with at least 20 Gy (FV20) and 30 Gy (FV30) by 26.02% ±15.45% and 14.41% ±16.66%, respectively, as compared to the seven-beam computed tomography (CT-7) plan. The CI significantly differed between the SPECT-7 and SPECT-4 plans and between the SPECT-5 and SPECT-4 plans, but not between the SPECT-5 and SPECT-7 plans. The CIs in the SPECT-5 and SPECT-7 plans were better than that in the SPECT-4 plan. The heterogeneity index significantly differed among the three SPECT plans and was best in the SPECT-7 plan.
Conclusions: The incorporation of SPECT images into IMRT planning for NSCLC greatly affected beam angles and number of beams. Fewer beams and modified beam angles achieved similar or better IMRT quality. The low-dose volumes were lower in SPECT-4.
Keywords: dosiometry beam angle; intensity-modulated radiation therapy; non-small lung carcinoma; number of beams.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intensity modulated radiotherapy of non-small-cell lung cancer incorporating SPECT ventilation imaging.Med Phys. 2010 Apr;37(4):1863-72. doi: 10.1118/1.3358128. Med Phys. 2010. PMID: 20443508
-
A methodology for selecting the beam arrangement to reduce the intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) dose to the SPECT-defined functioning lung.Phys Med Biol. 2010 Jan 21;55(2):403-16. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/2/005. Epub 2009 Dec 17. Phys Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20019404
-
A potential to reduce pulmonary toxicity: the use of perfusion SPECT with IMRT for functional lung avoidance in radiotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2007 May;83(2):156-62. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 May 9. Radiother Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17493699
-
Protection of lung function by introducing single photon emission computed tomography lung perfusion image into radiotherapy plan of lung cancer.Chin Med J (Engl). 2009 Mar 5;122(5):509-13. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009. PMID: 19323899
-
Poster - Thurs Eve-40: The potential of using SPECT ventilation information with IMRT for functional lung avoidance in radiotherapy of non small cell lung cancer.Med Phys. 2008 Jul;35(7Part3):3409. doi: 10.1118/1.2965959. Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 28512881
Cited by
-
Incorporation of Functional Lung Imaging Into Radiation Therapy Planning in Patients With Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024 Oct 1;120(2):370-408. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.04.001. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024. PMID: 38631538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Langfort R, Szołkowska M, Szczepulska-Wójcik E, Qandil N, Maksymiuk B, Giedronowicz D, Rudziński P, Orłowski TM. The importance of immunohistochemistry for differentiation of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in small samples and cytology specimens. Kardiochirur Torakochirur Pol. 2012;9:202–208.
-
- Arriagada R, Komaki R, Cox JD. Radiation dose escalation in non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004;14:287–91. - PubMed
-
- Graham MV, Purdy JA, Emami B, Harms W, Bosch W, Lockett MA, Perez CA. Clinical dose-volume histogram analysis for pneumonitis after 3d treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;45:323–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
