Incorporation of membrane-anchored flagellin or Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit enhances the immunogenicity of rabies virus-like particles in mice and dogs
- PMID: 25784906
- PMCID: PMC4347500
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00169
Incorporation of membrane-anchored flagellin or Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit enhances the immunogenicity of rabies virus-like particles in mice and dogs
Abstract
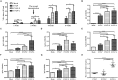
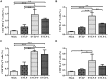
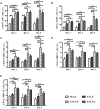
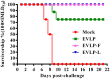
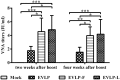
Rabies remains an important worldwide public health threat, so safe, effective, and affordable vaccines are still being sought. Virus-like particle-based vaccines targeting various viral pathogens have been successfully produced, licensed, and commercialized. Here, we designed and constructed two chimeric rabies virus-like particles (cRVLPs) containing rabies virus (RABV) glycoprotein (G), matrix (M) protein, and membrane-anchored flagellin (EVLP-F) or Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit (EVLP-L) as molecular adjuvants to enhance the immune response against rabies. The immunogenicity and potential of cRVLPs as novel rabies vaccine were evaluated by intramuscular vaccination in mouse and dog models. Mouse studies demonstrated that both EVLP-F and EVLP-L induced faster and larger virus-neutralizing antibodies (VNAs) responses and elicited greater numbers of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells secreting IFN-γ or IL-4 compared with a standard rabies VLP (sRVLP) containing only G and M. Moreover, cRVLPs recruited and/or activated more B cells and dendritic cells in inguinal lymph nodes. EVLP-F induced a strong, specific IgG2a response but not an IgG1 response, suggesting the activation of Th1 class immunity; in contrast, Th2 class immunity was observed with EVLP-L. The significantly enhanced humoral and cellular immune responses induced by cRVLPs provided complete protection against lethal challenge with RABV. Most importantly, dogs vaccinated with EVLP-F or EVLP-L exhibited increased VNA titers in sera and enhanced IFN-γ and IL-4 secretion from peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Taken together, these results illustrate that when incorporated into sRVLP, membrane-anchored flagellin, and heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit possess strong adjuvant activity. EVLP-F and EVLP-L induce significantly enhanced RABV-specific humoral and cellular immune responses in both mouse and dog. Therefore, these cRVLPs may be developed as safe and more efficacious rabies vaccine candidate for animals.
Keywords: LTB; flagellin; rabies vaccine; rabies virus; virus-like particle.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

