Association of three common BARD1 variants with cancer susceptibility: a system review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 25785002
- PMCID: PMC4358457
Association of three common BARD1 variants with cancer susceptibility: a system review and meta-analysis
Abstract
BARD1 has been shown to play tumor suppressive roles in human cancer. We performed this meta-analysis and firstly evaluated the association between three common BARD1 polymorphisms (Arg378Ser, Val507Met and Pro24Ser) and cancer susceptibility. We performed this meta-analysis following PRISMA guidelines. A comprehensive search of PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, OVID and Web of Science databases was done from database inception to August 2014. Odds ratios (ORs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were combined to measure the association between BARD1 polymorphisms and cancer risk. On the basis of 10 studies about BARD1 polymorphisms and cancer, we found that BARD1 Val507Met (G/A) polymorphism was associated with decreased cancer susceptibility (allelic model: OR = 0.76, 95% CI: 0.66-0.87, P < 0.00001; dominant model: OR = 0.77, 95% CI: 0.65-0.91, P < 0.00001; recessive model: OR = 0.64, 95% CI: 0.55-0.74, P < 0.00001; homozygote comparison: OR = 0.58, 95% CI: 0.49-0.70, P < 0.00001; heterozygote comparison: OR = 0.85, 95% CI: 0.74-0.99 , P = 0.0008). BARD1 Pro24Ser (C/T) polymorphism was also associated decreased cancer risk in allelic model (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.60-0.88, P = 0.0009), dominant model (OR = 0.70, 95% CI: 0.56-0.87, P = 0.004), recessive model (OR = 0.70, 95% CI: 0.56-0.87 , P = 0.004), homozygote comparison (OR = 0.55, 95% CI: 0.39-0.78, P = 0.0007) and heterozygote comparison (OR = 0.75, 95% CI: 0.62-0.91, P = 0.004). And in our sensitivity analysis, when deleting the study performed by Capasso in 2009, we found that BARD1 Arg378Ser polymorphism was associated with decreased cancer risk in allelic model (OR = 0.81, 95% CI: 0.67-0.97, P = 0.02), dominant model (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.56-0.91, P = 0.007) and heterozygote comparison (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.57-0.91, 0 = 0.006). In conclusion, BARD1 Arg378Ser, Val507Met and Pro24Ser may be associated with decreased cancer risk. More studies with larger samples and gene-environment interactions are needed to confirm our findings.
Keywords: BARD1; cancer risk; meta-analysis; polymorphism.
Figures
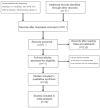
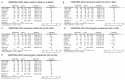
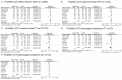
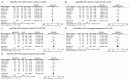

Similar articles
-
[Association between single nucleotide polymorphism of BARD1 gene and BRCA1 gene mutation in epithelial ovarian cancer].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jun 25;52(6):403-410. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567X.2017.06.009. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28647964 Chinese.
-
[Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms of BARD 1 gene and susceptibility of early-onset breast cancer in Uygur women in Xinjiang].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2012 May;34(5):341-7. doi: 10. 3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2012.05.005. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22883453 Chinese.
-
Common non-synonymous polymorphisms in the BRCA1 Associated RING Domain (BARD1) gene are associated with breast cancer susceptibility: a case-control analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007 May;102(3):329-37. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9332-7. Epub 2006 Sep 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007. PMID: 17028982
-
Association of β2-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphisms (rs1042713, rs1042714, rs1042711) with asthma risk: a systematic review and updated meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Nov 7;19(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-0962-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2019. PMID: 31699066 Free PMC article.
-
CAV1 polymorphisms rs1049334, rs1049337, rs7804372 might be the potential risk in tumorigenicity of urinary cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Jan;215(1):151-158. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.11.009. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 30463805
Cited by
-
DNA damage and repair (DDR) gene mutation profiles in driver gene wild-type advanced non-small cell lung cancer and the predictive role of response to platinum-based chemotherapy.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):1089-1103. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-972. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40386740 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-exome Sequencing of Nigerian Prostate Tumors from the Prostate Cancer Transatlantic Consortium (CaPTC) Reveals DNA Repair Genes Associated with African Ancestry.Cancer Res Commun. 2022 Sep 16;2(9):1005-1016. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0136. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cancer Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36922933 Free PMC article.
-
BARD1 Gene Polymorphisms Confer Nephroblastoma Susceptibility.EBioMedicine. 2017 Feb;16:101-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.01.038. Epub 2017 Jan 31. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 28161399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu LC, Wang ZW, Tsan JT, Spillman MA, Phung A, Xu XL, Yang MC, Hwang LY, Bowcock AM, Baer R. Identification of a RING protein that can interact in vivo with the BRCA1 gene product. Nat Genet. 1996;14:430–440. - PubMed
-
- Irminger-Finger I. BARD1, a possible biomarker for breast and ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;117:211–215. - PubMed
-
- Birrane G, Varma AK, Soni A, Ladias JA. Crystal structure of the BARD1 BRCT domains. Biochemistry. 2007;46:7706–7712. - PubMed
-
- Simons AM, Horwitz AA, Starita LM, Griffin K, Williams RS, Glover JN, Parvin JD. BRCA1 DNA-binding activity is stimulated by BARD1. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2012–2018. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
