Ghrelin inhibits AngII -induced expression of TNF-α, IL-8, MCP-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 25785032
- PMCID: PMC4358487
Ghrelin inhibits AngII -induced expression of TNF-α, IL-8, MCP-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
Aim: Ghrelin, a gastric peptide, is involved in several metabolic and cardiovascular processes. Emerging evidence indicates the potential involvement of ghrelin in low-grade inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis and hypertension. Cytokine-induced inflammation is critical in these pathological states. The growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) has been identified in blood vessels, so we predict that ghrelin might inhibit proinflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). The aim of this study is to examine the effect of ghrelin on angiotension II (AngII)-induced expression of TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-8 in HUVECs.
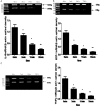
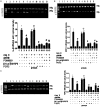
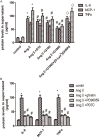
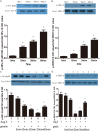
Method: HUVECs were pretreated with ghrelin, with or without the specific antagonist of GHSR [D-Lys(3)]-GHRP-6, the selective inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) PDTC, and the selective inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) PD98059. The cells were finally treated with AngII. The expression of TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-8 was examined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The activity of ERK1/2 and NF-κB was analyzed by Western blot.
Result: our study showed that ghrelin inhibited AngII -induced expression of IL-8, TNF-α and MCP-1 in the HUVECs via GHSR pathway in concentration- and time-dependent manners. We also found that ghrelin inhibited AngII -induced activation of ERK1/2 and NF-κB.
Conclusions: these results suggest that Ghrelin may play novel antiinflammatory and immunoregulatory roles in HUVECs.
Keywords: Ghrelin; NF-κB and MAPK pathways; atherosclerosis; inflammation; interleukin-8; monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human endothelial cells.Circulation. 2004 May 11;109(18):2221-6. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000127956.43874.F2. Epub 2004 Apr 26. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15117840
-
Effect of ghrelin on angiotensin II induced human umbilicus vein endothelial cell oxidative stress and endothelial cell injury.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010 Oct;35(10):1037-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2010.10.003. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010. PMID: 21051828
-
Ghrelin alleviates neuropathic pain through GHSR-1a-mediated suppression of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway in a rat chronic constriction injury model.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2014 Mar-Apr;39(2):137-48. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000050. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2014. PMID: 24513955
-
Carnosol inhibits cell adhesion molecules and chemokine expression by tumor necrosis factor-α in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through the nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Feb;9(2):476-80. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1839. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24316968
-
Effect of caffeic acid on tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced vascular inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Aug;32(8):1371-7. doi: 10.1248/bpb.32.1371. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009. PMID: 19652376
Cited by
-
Regulation of Ghrelin Receptor by Periodontal Bacteria In Vitro and In Vivo.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:4916971. doi: 10.1155/2017/4916971. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29317796 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of isotretinoin on body mass index, serum adiponectin, leptin, and ghrelin levels in acne vulgaris patients.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2016 Aug;33(4):294-9. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2016.56928. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2016. PMID: 27605902 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin Downregulates Lipopolysaccharide/ Leptin-Induced MUC5AC Expression in Human Nasal Epithelial Cells.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Feb;16(1):49-58. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2022.00857. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36177976 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin Fights Against Titanium Particle-Induced Inflammatory Osteolysis Through Activation of β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2019 Oct;42(5):1652-1665. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01026-w. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31165326
-
The potential probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-3690 strain protects the intestinal barrier by stimulating both mucus production and cytoprotective response.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 1;9(1):5398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41738-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30931953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–60. - PubMed
-
- Tang NP, Wang LS, Yang L, Gu HJ, Zhu HJ, Zhou B, Sun QM, Cong RH, Wang B. Preproghrelin Leu72Met polymorphism in Chinese subjects with coronary artery disease and controls. Clin Chim Acta. 2008;387:42–7. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Fang WY, Yuan F, Qu XK, Liu H, Xu YJ, Chen H, Yu YF, Shen Y, Zheng ZC. Plasma ghrelin levels are closely associated with severity and morphology of angiographically-detected coronary atherosclerosis in Chinese patients with diabetes mellitus. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012;33:452–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Ren Y, Liu X, Li WG, Yang J, Geng B, Weintraub NL, Tang C. Protective effects of ghrelin on ischemia/reperfusion injury in the isolated rat heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2004;43:165–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
