The expression and correlation of SIRT1 and Phospho-SIRT1 in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 25785061
- PMCID: PMC4358516
The expression and correlation of SIRT1 and Phospho-SIRT1 in colorectal cancer
Abstract
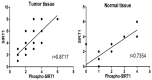
SIRT1 is the homologue of sir2 in mammals, which is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)) dependent histone deacetylase. SIRT1 is involved in many physiological processes, such as metabolism, senescence, inflammatory response, neuroprotection, and tumorigenesis by acetylating histones and multiple transcription factors. However, the exact role of SIRT1 in tumor is still under controversial. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot were performed to investigate the expressions and subcellular localizations of SIRT1 and Phospho-SIRT1 in colorectal cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues. The relationship between SIRT1 or Phospho-SIRT1 and clinicopathological characteristics was also analyzed. Real-Time PCR was performed to investigate the transcriptional level of SIRT1 mRNA in colorectal cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues. SIRT1 and Phospho-SIRT1 were both localized in the nucleus. The expressions of SIRT1 and Phospho-SIRT1 were higher in colorectal cancer tissues than normal tissues. SIRT1 expression in cancer tissues was associated with patient age, TNM stage and mutant P53 loss. Phospho-SIRT1 expression in cancer tissues was associated with Ki67. SIRT1 and Phospho-SIRT1 were highly correlated in cancer tissues and normal tissues. The ratios of Phospho-SIRT1 and SIRT1 expression in cancer tissues were higher than normal tissues. SIRT1 mRNA level was no significant difference in cancer tissues and normal tissues. SIRT1 have a dual character in colorectal cancer, and Phospho-SIRT1 may determine the role of SIRT1 in colorectal cancer formation.
Keywords: Ki67; P53; Phospho-SIRT1; SIRT1; colorectal cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Survival and Clinicopathological Significance of SIRT1 Expression in Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Mar 13;10:121. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00121. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30930849 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of SIRT1 histone deacetylase expression associates with tumour progression in colorectal adenocarcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2012 Aug;65(8):735-9. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-200685. Epub 2012 May 3. J Clin Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22554968
-
Sirt1 is a tumor promoter in lung adenocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2014 Jul;8(1):387-393. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2057. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24959282 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and Predictive Role of Sirtuin1 Expression in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Clin Lab. 2016 Oct 1;62(10):1989-1994. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2016.160317. Clin Lab. 2016. PMID: 28164517
-
Role of Sirtuin1-p53 regulatory axis in aging, cancer and cellular reprogramming.Ageing Res Rev. 2018 May;43:64-80. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2018.02.004. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Ageing Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29476819 Review.
Cited by
-
SIRT1 controls cell proliferation by regulating contact inhibition.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Sep 16;478(2):868-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.041. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27514448 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Post-translational Modification of Silent Mating Type Information Regulator 2 Homolog 1 in Cancer and Other Disorders.J Cancer Prev. 2022 Sep 30;27(3):157-169. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2022.27.3.157. J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 36258719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-133b inhibits glioma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Sirt1.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):36247-36254. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9198. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27166997 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation and migration of malignant melanoma cells via targeting sirituin 1.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Aug;14(2):931-938. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4595. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Exp Ther Med. 2017. Retraction in: Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1135. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10569. PMID: 28810544 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Survival and Clinicopathological Significance of SIRT1 Expression in Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Mar 13;10:121. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00121. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30930849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fessel MR, Lira CB, Giorgio S, Ramos CH, Cano MI. Sir2-Related Protein 1 from Leishmania amazonensis is a glycosylated NAD+-dependent deacetylase. Parasitology. 2011;138:1245–1258. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
