A new model for the discrimination between ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
- PMID: 25785066
- PMCID: PMC4358521
A new model for the discrimination between ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
Abstract
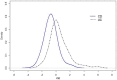
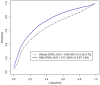
Distinguishing ulcerative colitis (UC) from Crohn's disease (CD) is sometimes difficult in a clinical setting. The purpose of this study was to identify a series of independent serum markers capable of distinguishing between UC and CD. 140 UC and 174 CD patients hospitalized at The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University were recruited into this study. A panel of serum markers was quantified for each patient and the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) was used to determine a discrimination model. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) was used to evaluate the performance of the model, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the accuracy of the model. Serum albumin (Alb), total cholesterol (TC), total calcium (TCa), platelet (Plt), glycyl proline dipeptidyl aminopeptidase (GPDA) and their ratios (Alb: Plt, Alb: GPDA, TCa: TC, and Plt: GPDA) were selected into the diagnosis model using BIC. The resulting CD/UC Index (CUI) is CUI = 1.901 + 0.425 Alb - 3.324 TC - 7.444 TCa + 0.018 Plt + 0.087 GPDA - 0.0007 Alb: Plt - 0.004 Alb: GPDA + 1.839 TC: TCa + 0.003 Plt: GPDA, with CUI > 0 incrementally favored a diagnosis of UC, while CUI < 0 corresponded to a higher likelihood of a diagnosis of CD. An average value of the AUC for the CUI model is 0.73 (95% confidence interval: 0.67-0.80). The CUI, derived from commonly available serum biomarkers, could try to differentiate UC from CD in patients with unclear clinical features as a new approach to diagnosis.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Ulcerative colitis; diagnostic model; serum biomarkers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Platelet/Albumin ratio and plateletcrit levels are potential new biomarkers for assessing endoscopic inflammatory bowel disease severity.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Nov 14;23(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-03043-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37964205 Free PMC article.
-
Fragments of Citrullinated and MMP-degraded Vimentin and MMP-degraded Type III Collagen Are Novel Serological Biomarkers to Differentiate Crohn's Disease from Ulcerative Colitis.J Crohns Colitis. 2015 Oct;9(10):863-72. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv123. Epub 2015 Jul 17. J Crohns Colitis. 2015. PMID: 26188349 Clinical Trial.
-
Platelets can reflect the severity of Crohn's disease without the effect of anemia.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2020;75:e1596. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2020/e1596. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2020. PMID: 32667493 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating ulcerative colitis from Crohn disease in children and young adults: report of a working group of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007 May;44(5):653-74. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31805563f3. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17460505
-
Laboratory markers in ulcerative colitis: Current insights and future advances.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015 Feb 15;6(1):13-22. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i1.13. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25685607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vermeire S, Van Assche G, Rutgeerts P. C-reactive protein as a marker for inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2004;10:661–5. - PubMed
-
- Palmon R, Brown SJ, Abreu MT. What is the role and significance of serum and stool biomarkers in the diagnosis of IBD? Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14(Suppl 2):S187–9. - PubMed
-
- Mendoza JL, Abreu MT. Biological markers in inflammatory bowel disease: Practical consideration for clinicians. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2009;33(Suppl 3):S158–73. - PubMed
-
- Sappati Biyyani RS, Putka BS, Mullen KD. Dyslipidemia and lipoprotein profiles in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Lipidol. 2010;4:478–82. - PubMed
-
- Etzel JP, Larson MF, Anawalt BD, Collins J, Dominitz JA. Assessment and management of low bone density in inflammatory bowel disease and performance of professional society guidelines. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17:2122–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous