A memristor SPICE model accounting for synaptic activity dependence
- PMID: 25785597
- PMCID: PMC4364709
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120506
A memristor SPICE model accounting for synaptic activity dependence
Abstract
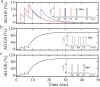
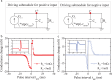
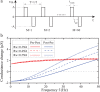
In this work, we propose a new memristor SPICE model that accounts for the typical synaptic characteristics that have been previously demonstrated with practical memristive devices. We show that this model could account for both volatile and non-volatile memristance changes under distinct stimuli. We then demonstrate that our model is capable of supporting typical STDP with simple non-overlapping digital pulse pairs. Finally, we investigate the capability of our model to simulate the activity dependence dynamics of synaptic modification and present simulated results that are in excellent agreement with biological results.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Memristive Hebbian plasticity model: device requirements for the emulation of Hebbian plasticity based on memristive devices.IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2015 Apr;9(2):197-206. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2015.2410811. Epub 2015 Apr 14. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2015. PMID: 25879966
-
Neuronal synapse as a memristor: modeling pair- and triplet-based STDP rule.IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2015 Feb;9(1):87-95. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2014.2318012. Epub 2014 Jun 20. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2015. PMID: 24960611
-
Synaptic modifications depend on synapse location and activity: a biophysical model of STDP.Biosystems. 2005 Jan-Mar;79(1-3):3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2004.09.010. Biosystems. 2005. PMID: 15649584
-
Synaptic plasticity: a unifying model to address some persisting questions.Int J Neurosci. 2011 Jun;121(6):289-304. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2011.556283. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Int J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21348800 Review.
-
Synaptic plasticity: taming the beast.Nat Neurosci. 2000 Nov;3 Suppl:1178-83. doi: 10.1038/81453. Nat Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11127835 Review.
Cited by
-
Emulating short-term synaptic dynamics with memristive devices.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 4;6:18639. doi: 10.1038/srep18639. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26725838 Free PMC article.
-
Low-power artificial neuron networks with enhanced synaptic functionality using dual transistor and dual memristor.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 27;20(1):e0318009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318009. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39869556 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of Neuro-Memristive Synapse for Long-and Short-Term Bio-Synaptic Plasticity.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jan 18;21(2):644. doi: 10.3390/s21020644. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33477650 Free PMC article.
-
Unsupervised learning in probabilistic neural networks with multi-state metal-oxide memristive synapses.Nat Commun. 2016 Sep 29;7:12611. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12611. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27681181 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Plasticity: From Molecules to Computation and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 6;21(5):1805. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051805. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32155701 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berdan R, Lim C, Khiat A, Papavassiliou C, Prodromakis T. A Memristor SPICE Model Accounting for Volatile Characteristics of Practical ReRAM. Electron Device Letters, IEEE. 2014;35: 135–137.
-
- Wang ZQ, Xu HY, Li XH, Yu H, Liu YC, et al. Synaptic learning and memory functions achieved using oxygen ion migration/diffusion in an amorphous InGaZnO memristor. Advanced Functional Materials. 2012;22: 2759–2765.
-
- Chua L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory. 1971;18: 507.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

